Humerus
This page is being worked on.
Content may be incomplete, improperly formatted, or inaccurate.
Goal: Understand how the humerus (hover for more information) relates to the body as a whole.
Purpose: To encourage deeper, longer-lasting learning by linking the bone to the skeletal, muscular, and cardiovascular systems rather than relying on rote memorization.
How to use this guide: Follow the five structured steps below. They are designed to help you focus on meaningful connections rather than on just memorizing facts.
Click to read about the five steps. Then click to close.
Each step relates the bone to the bigger picture to help you understand the material and remember it for longer.
Location
- Question: Where is the bone?
- Purpose: Helps you build a mental map of the skeleton.
Shape
- Question: What is the bone's shape?
- Purpose: Gives insight into how the bone interacts with the body.
Neighbors
- Question: What bones articulate (form joints with) this bone? What is the type of each joint?
- Purpose: Lets you examine what joints the bone is part of and what movements those joints allow.
Anatomical Landmarks
- Question: What are the named parts of the bone? What is the significance of each?
- Purpose: Connects each named location to the muscles, nerves, blood vessels, and other bones that interact with the location.
Blood Supply
- Question: What blood vessels nourish the bone?
- Purpose: Relates the bone to the cardiovascular system and builds your mental map of the body's blood vessels.
Step 1 – Location
The humerus is found in the upper arm between the shoulder and elbow.
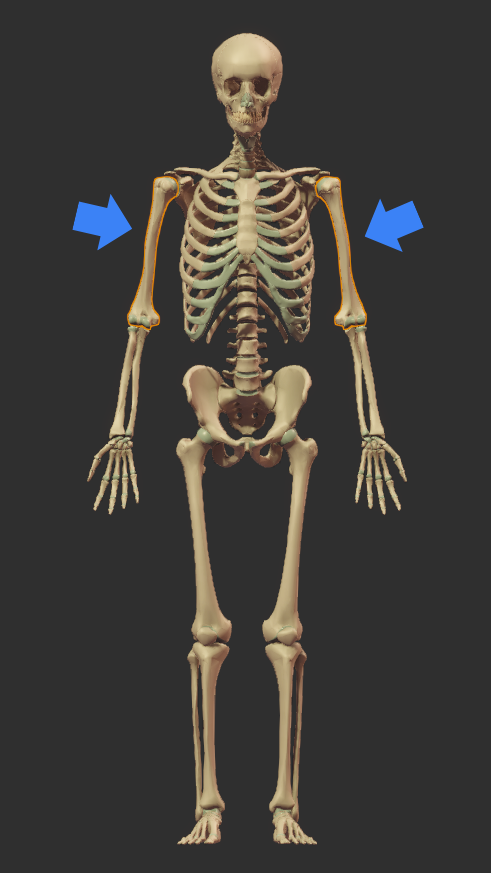
Right click image to enlarge.
Step 2 – Shape
The humerus is a long bone, which means it functions as a lever to enable movement of the arm.
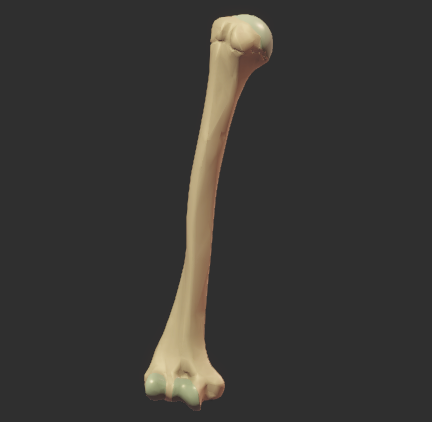
Right click image to enlarge.
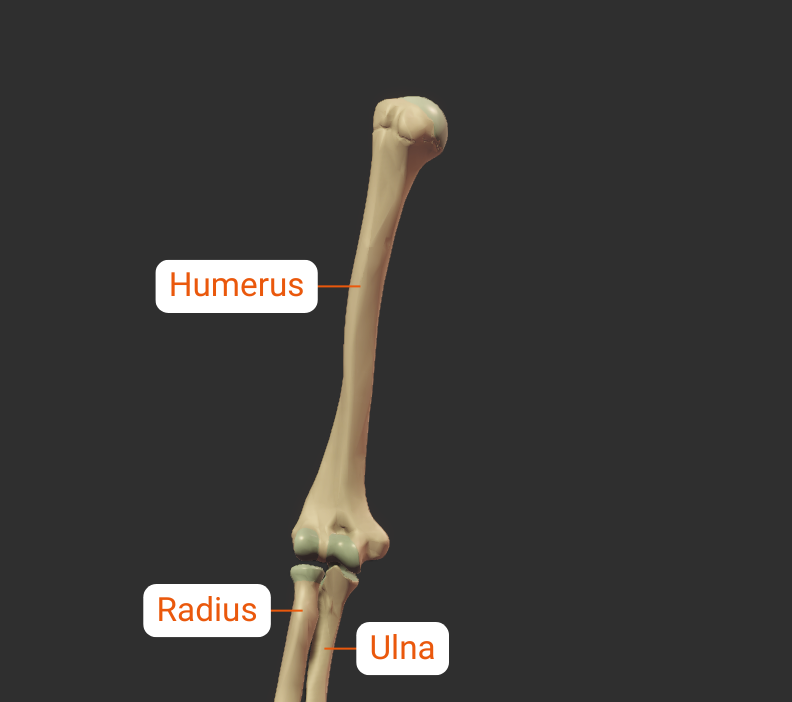
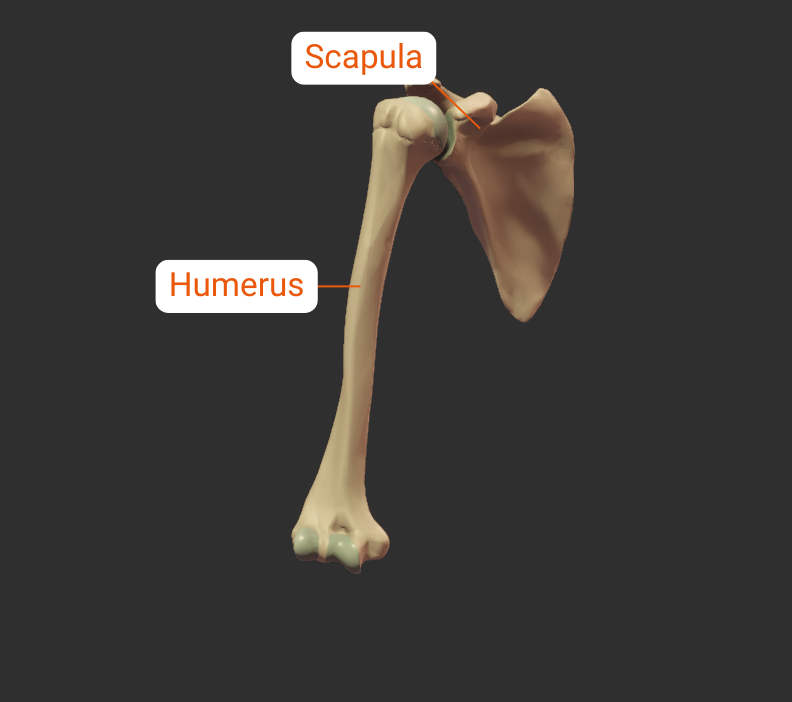
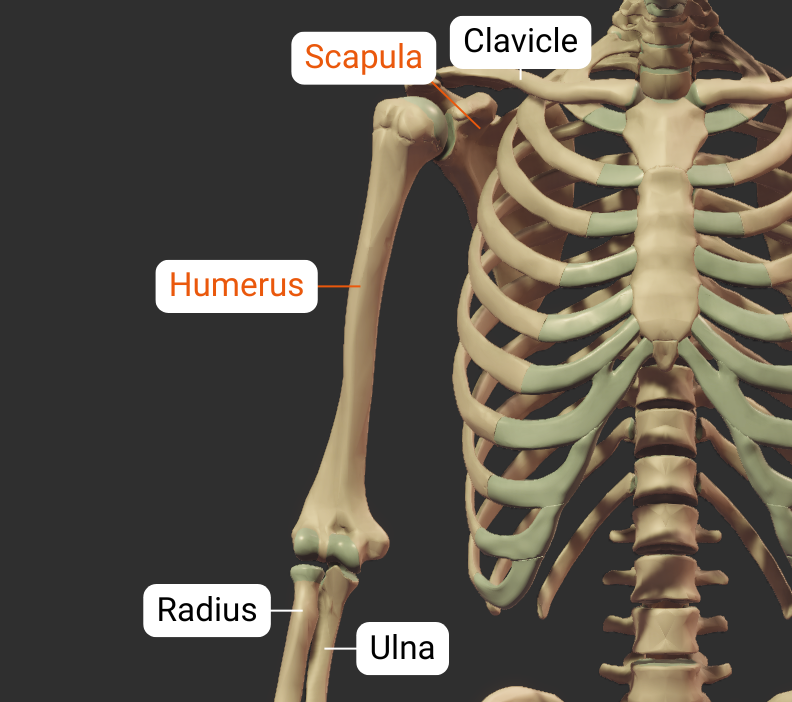
Step 3 – Neighbors
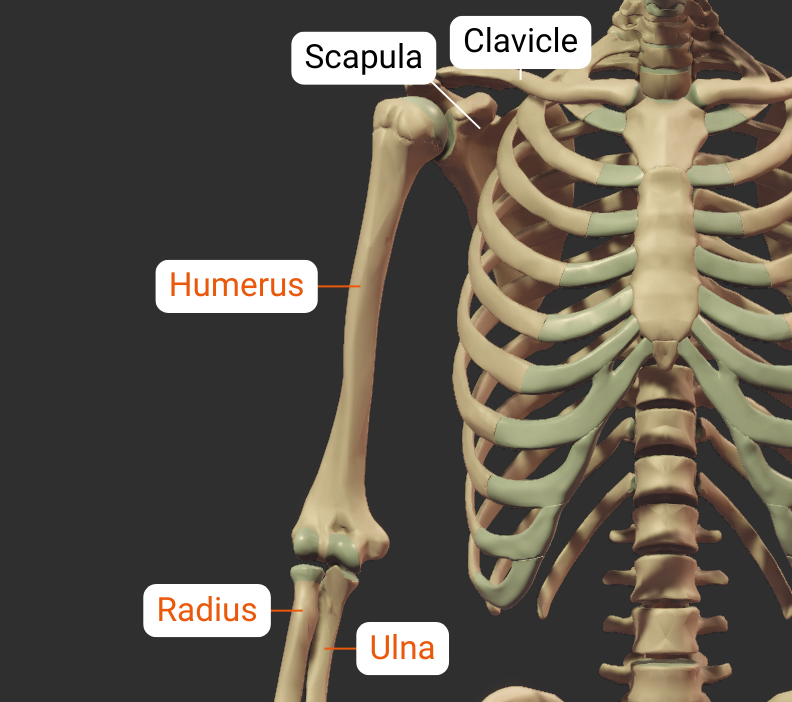
The humerus has neighboring bones at its two ends: the proximal end at the shoulder, and the distal end at the elbow.
Proximal
Click the bulleted names for more information.
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
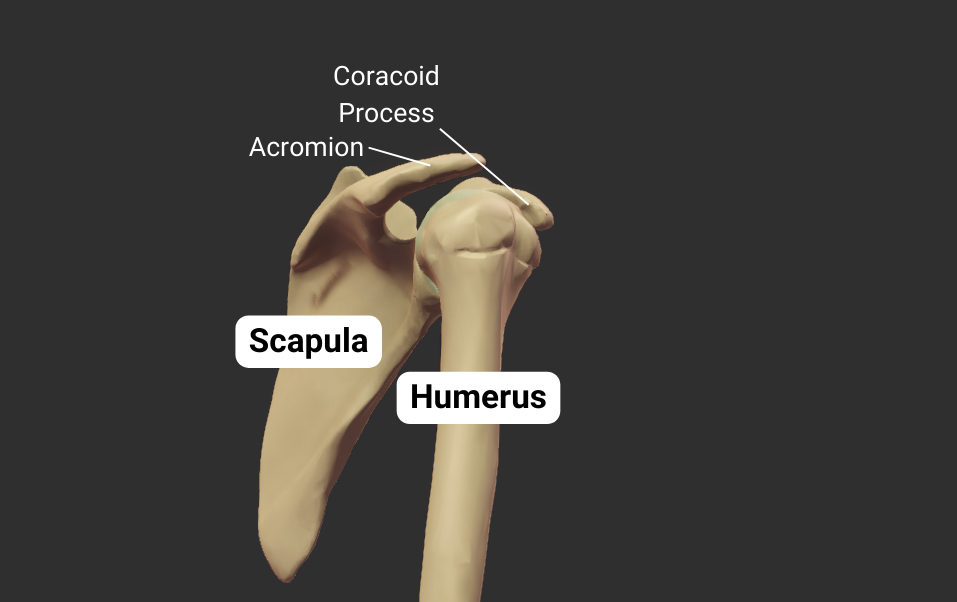
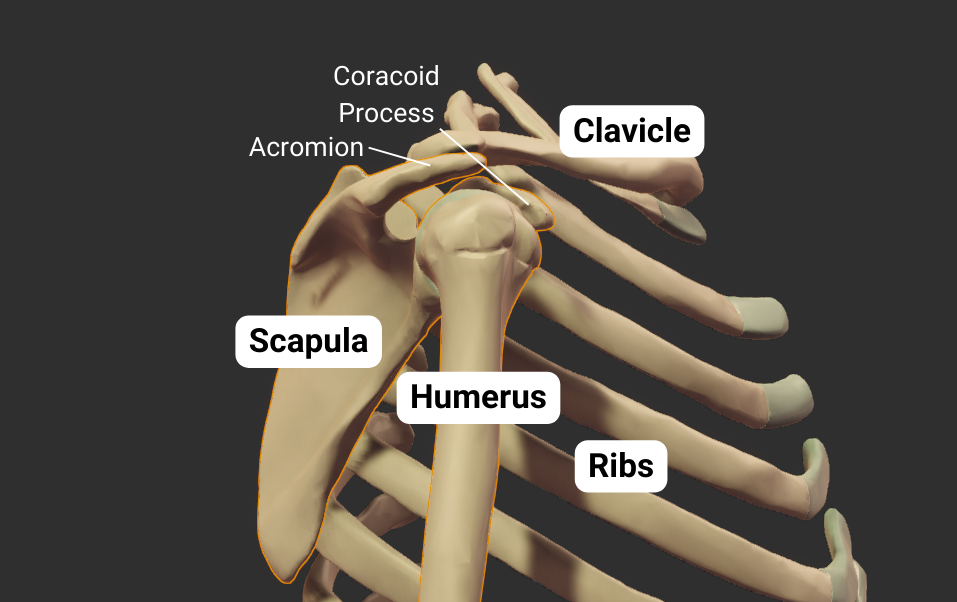
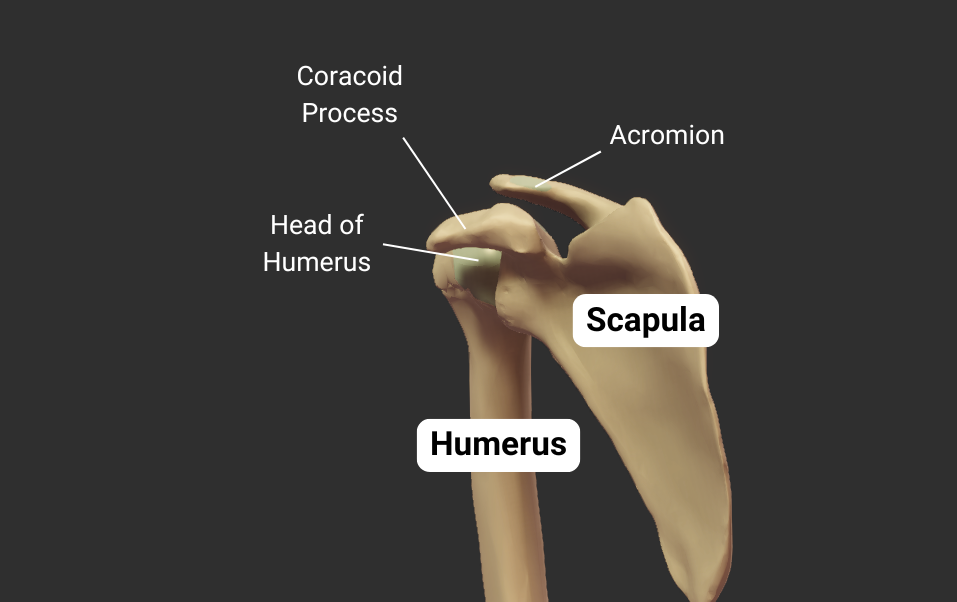
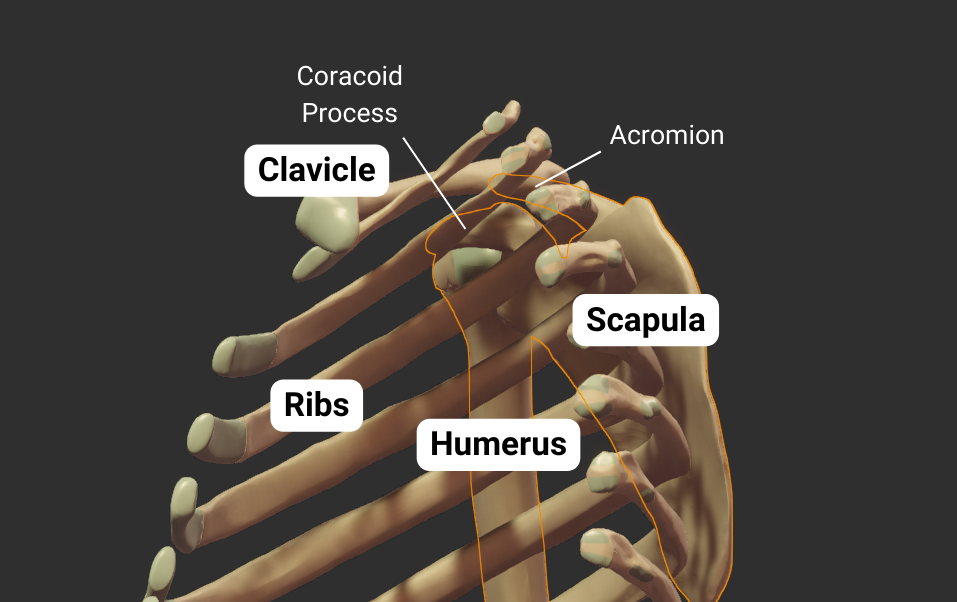
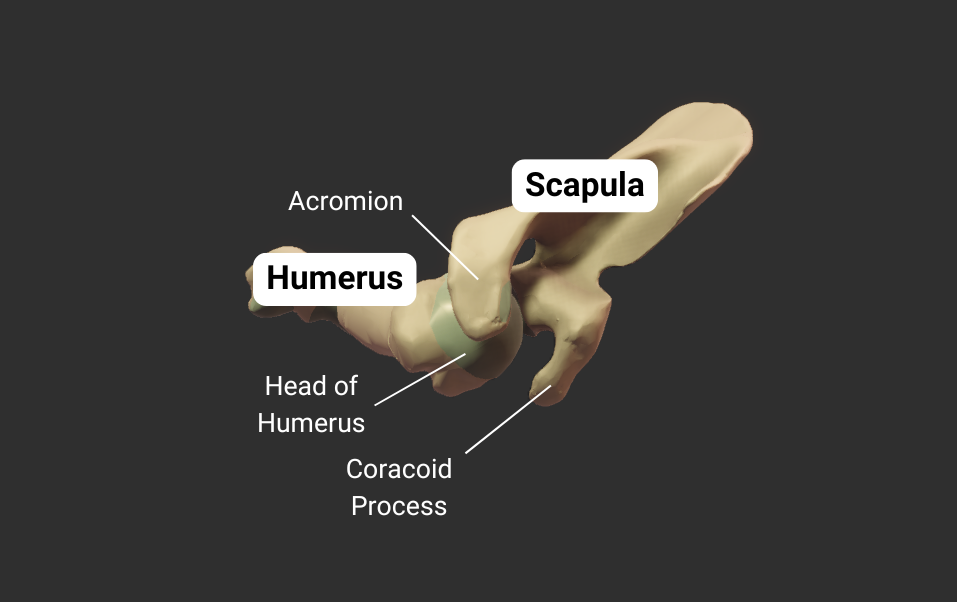
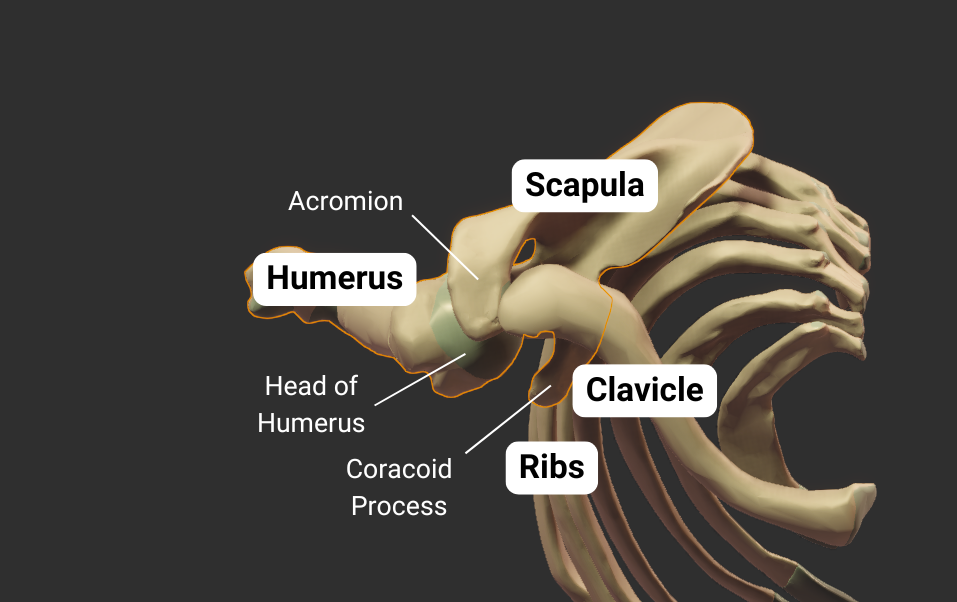
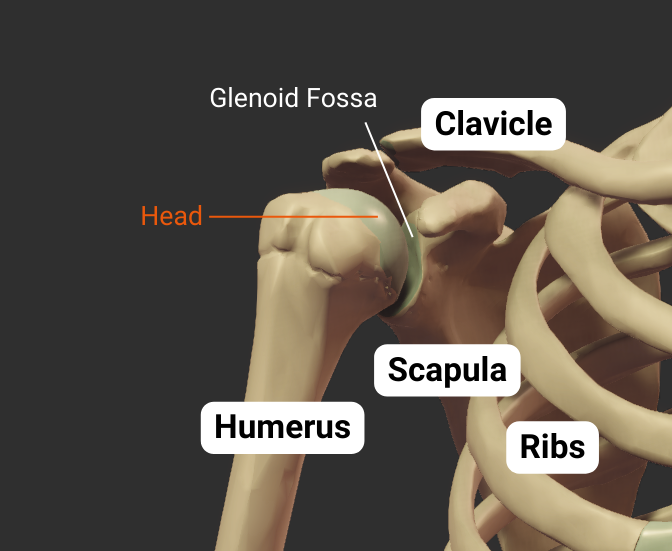
Scapula
Glenohumeral Joint
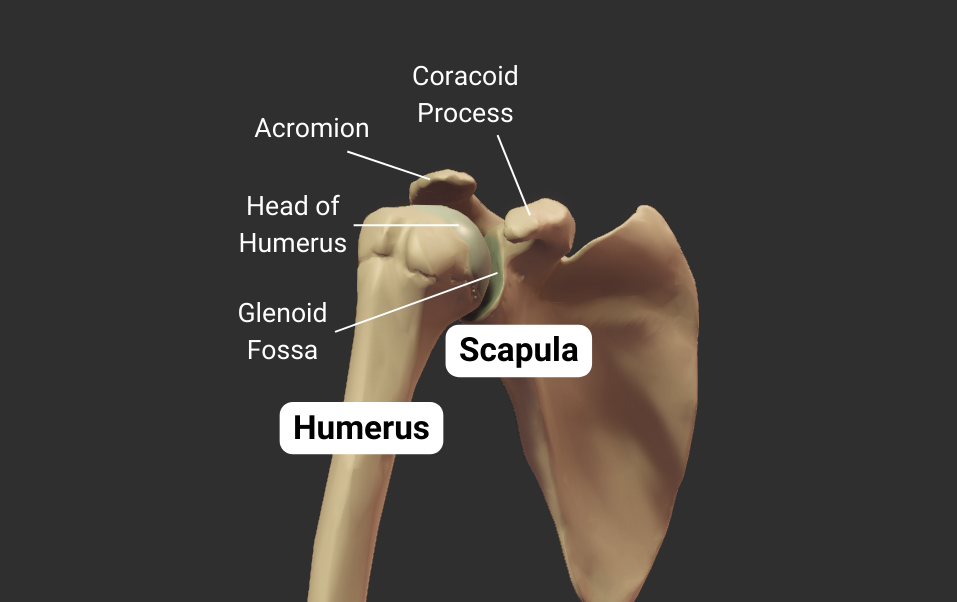
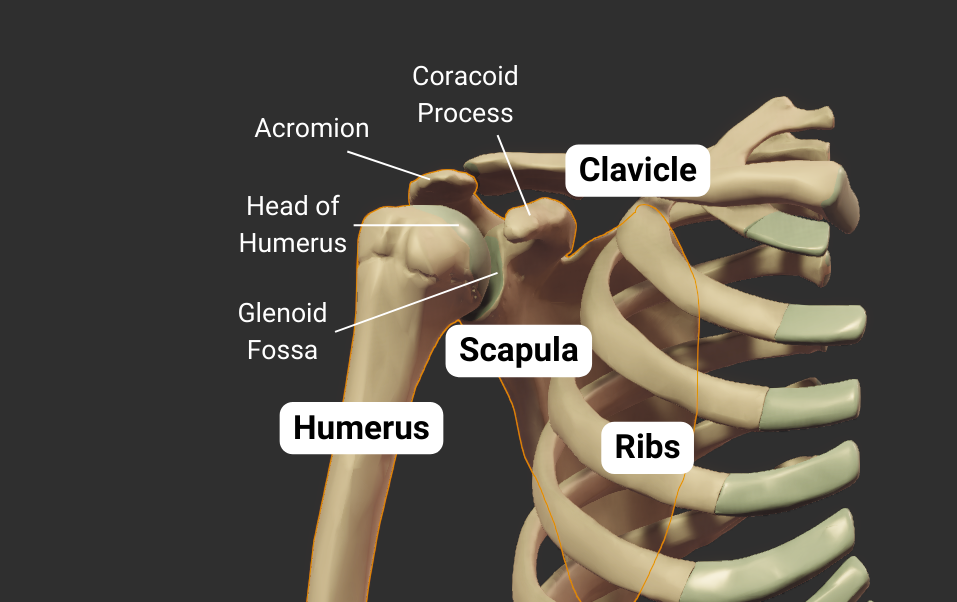
The humerus's head articulates with the scapula's glenoid fossa, forming the glenohumeral joint:
- Humeral head: spherical, like a ball
- Glenoid fossa: a socket, concave like a cup
- Joint type: synovial ball-and-socket
- Allowed motion: circumduction and rotation
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
Distal
Radius
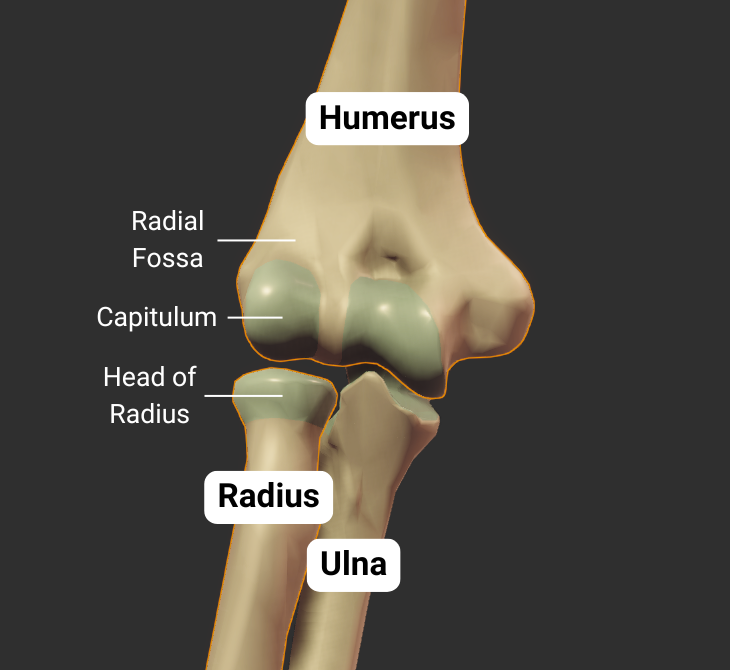
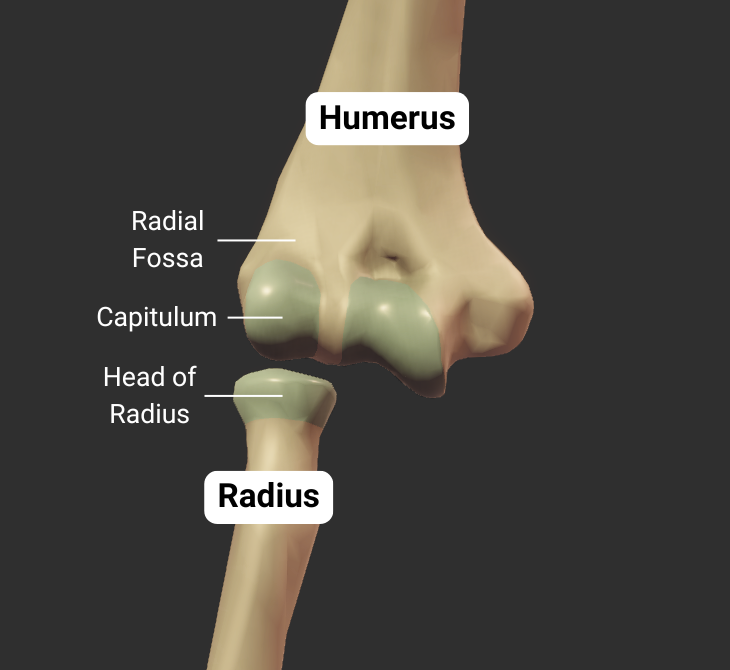
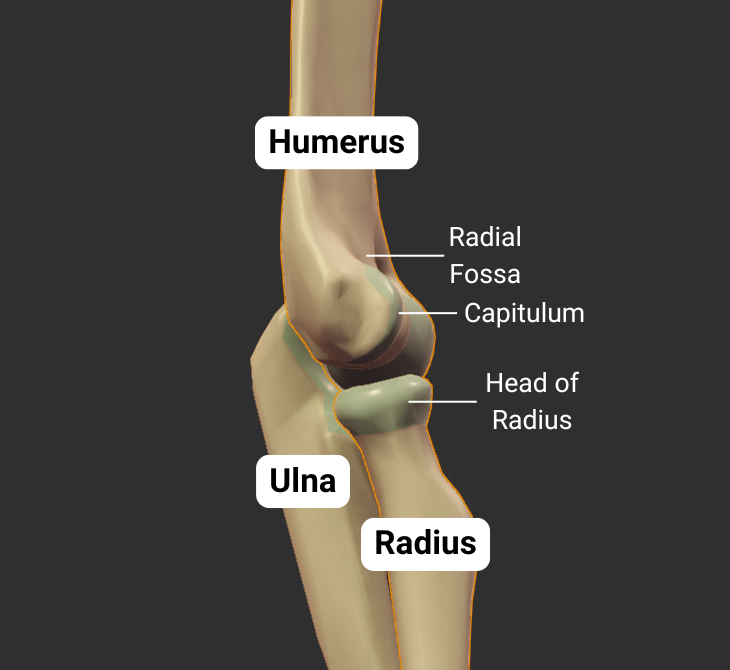
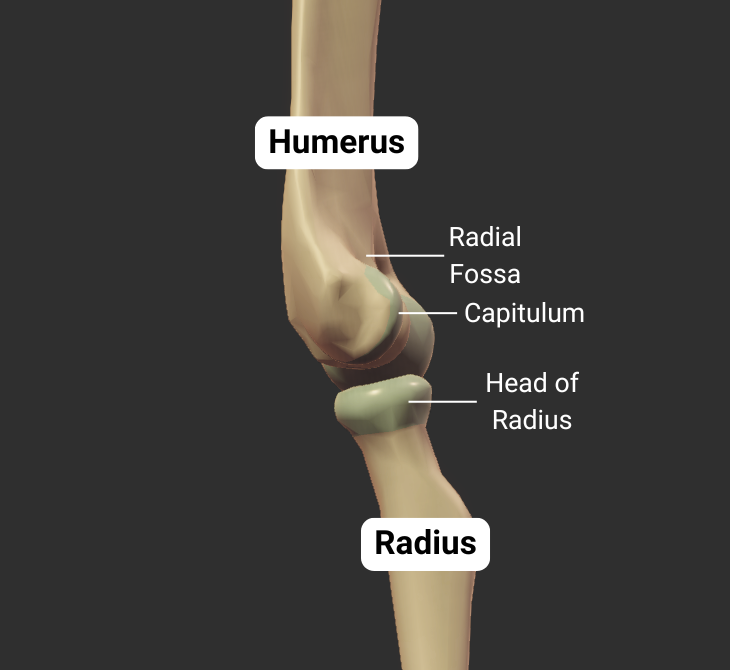
Humeroradial Joint - Part of Elbow Joint
The humerus's capitulum articulates with the radius's head, forming the humeroradial joint:
- Humeral capitulum: rounded
- Radial head: concave
- Joint type: synovial pivot
- Allowed motion: pronation, supination, flexion, and extension of the forearm
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
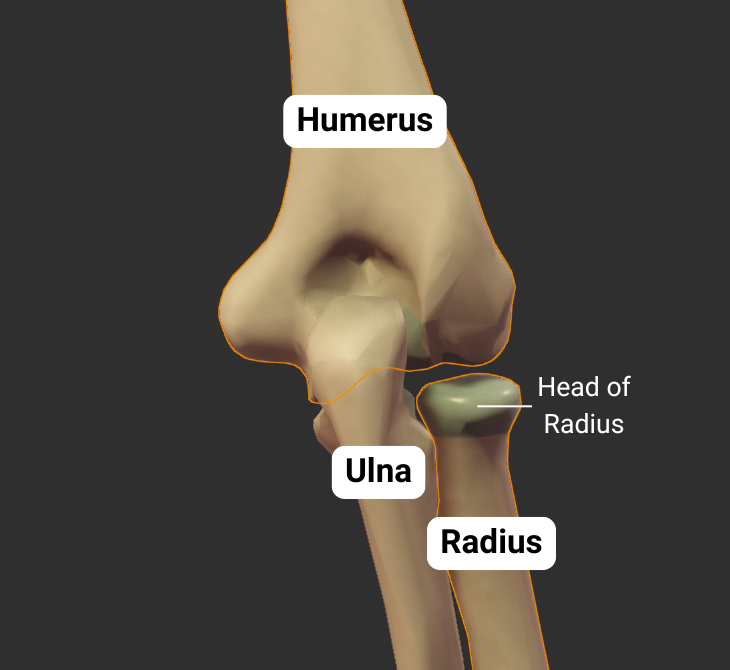
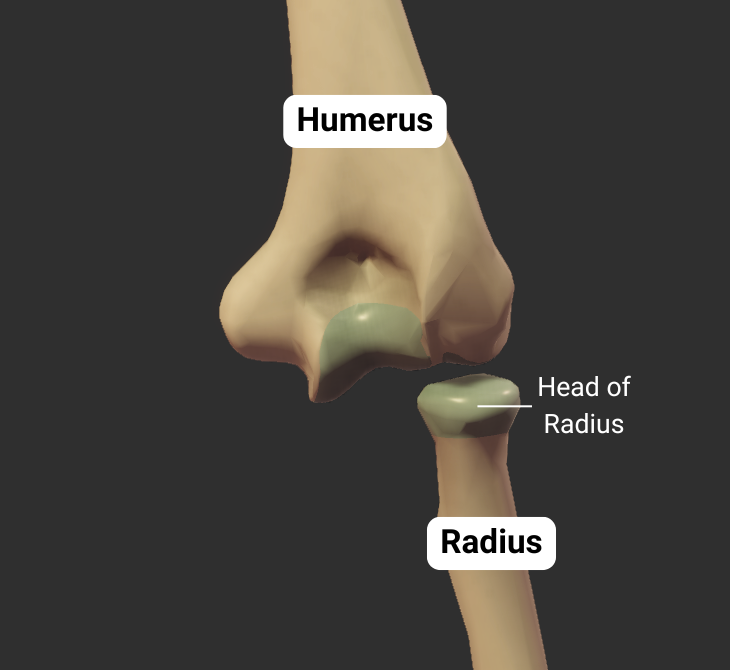
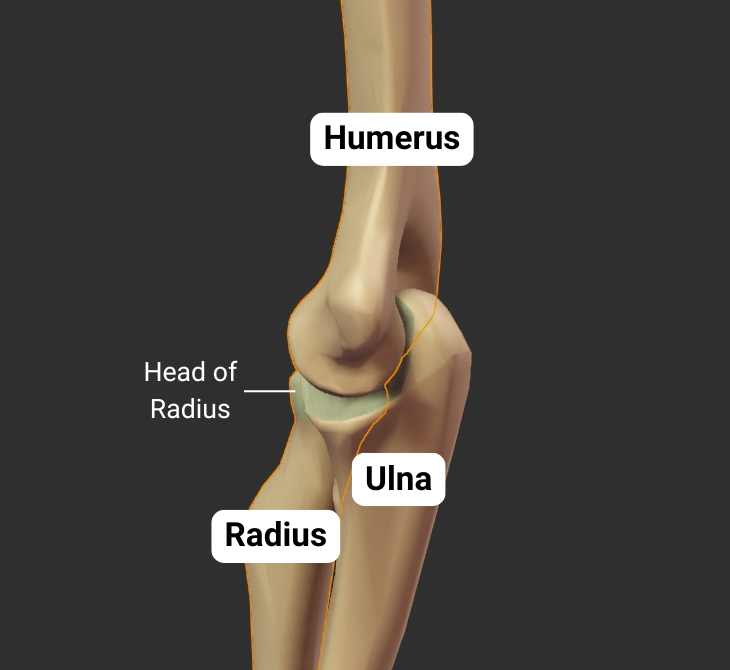
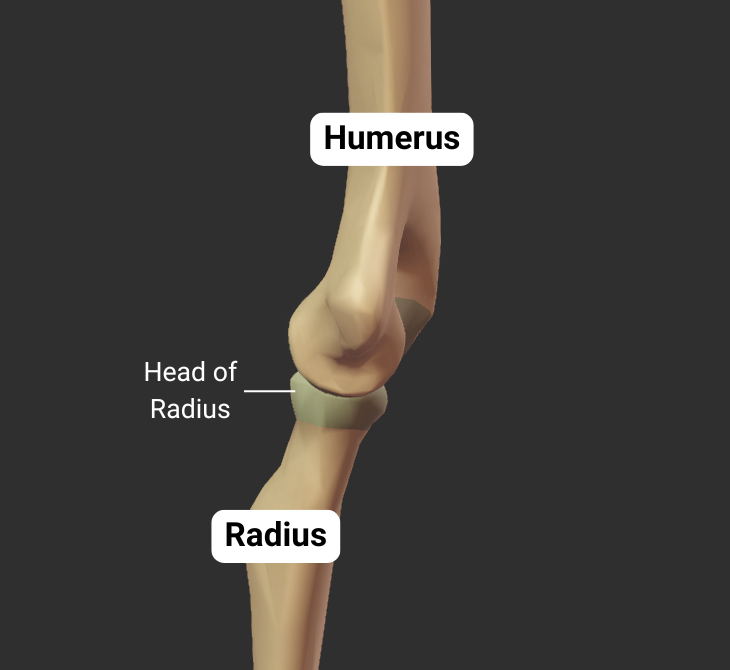
Ulna
Humeroulnar Joint - Part of Elbow Joint
The humerus's trochlea articulates with the ulna's trochlear notch, forming the humeroulnar joint:
- Humeral trochlea: cylindrical structure narrower in the middle than on the outside (like an hourglass)
- Ulnar trochlear notch: C-shaped, wraps around humeral trochlea
- Joint type: synovial hinge
- Allowed motion: flexion and extension of the forearm
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
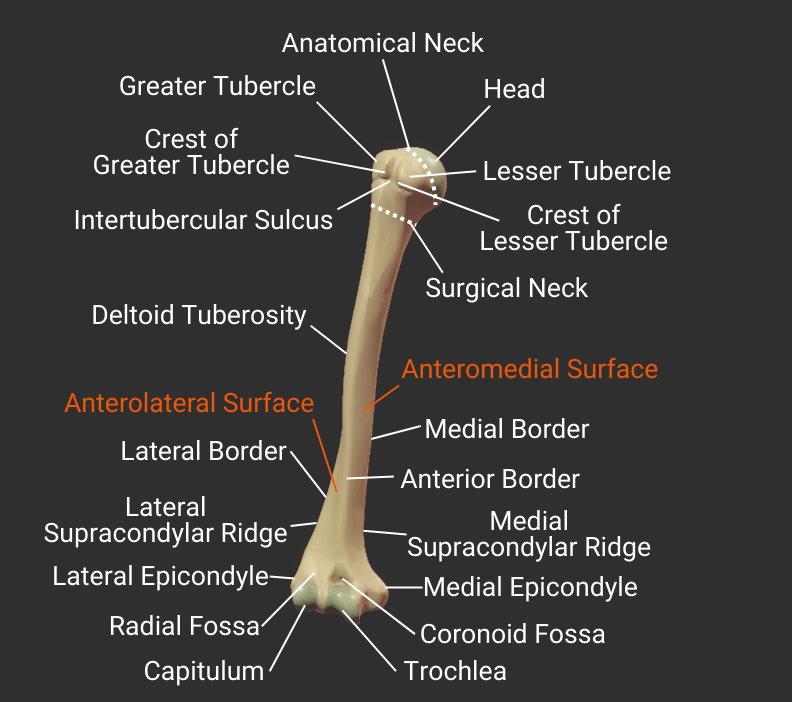
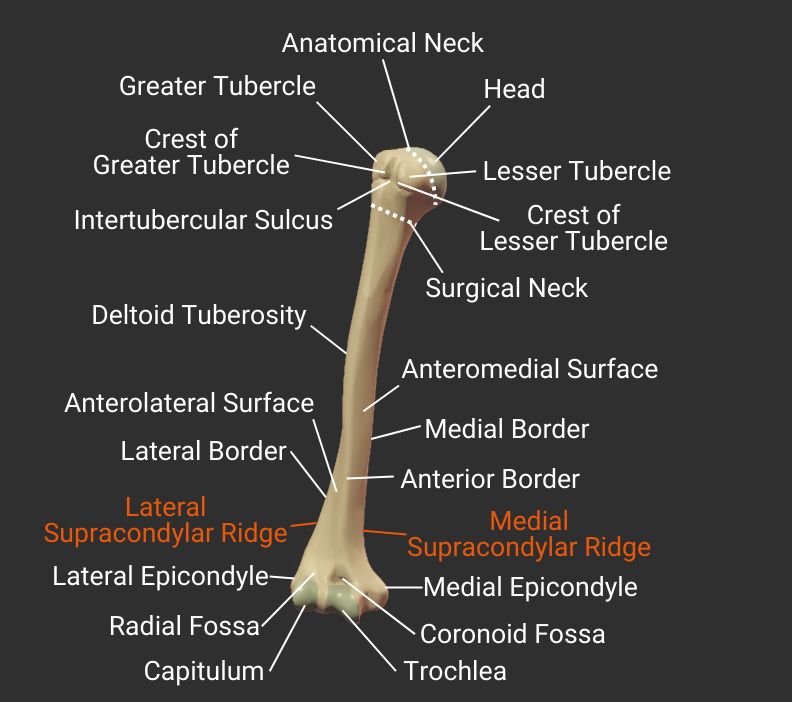
Step 4 – Anatomical Landmarks
Most of the named landmarks on the humerus are sites of muscle attachment. Some are grooves that guide tendons, nerves, and blood vessels. Others are indentations (fossas) that accomodate parts of neighboring bones during movement.
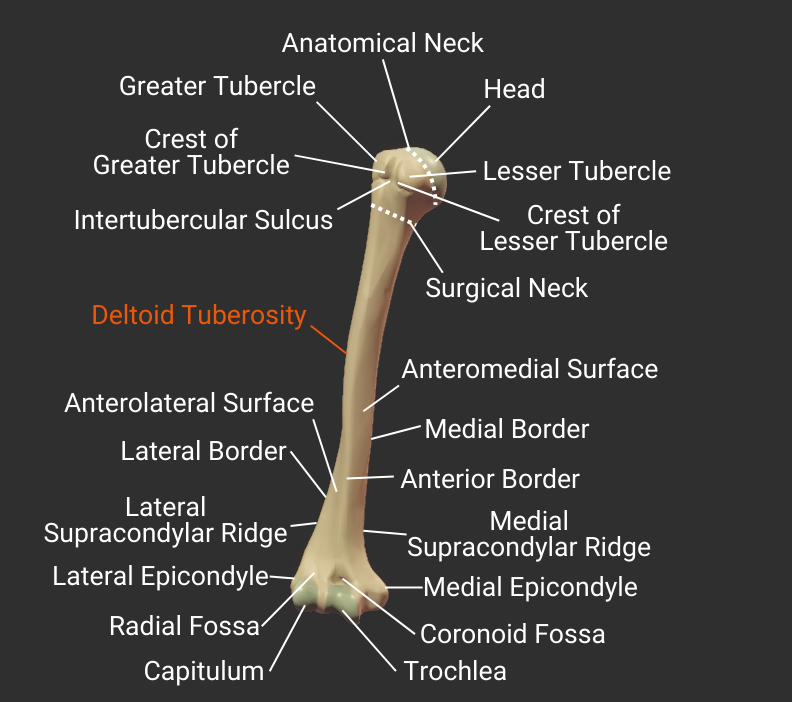
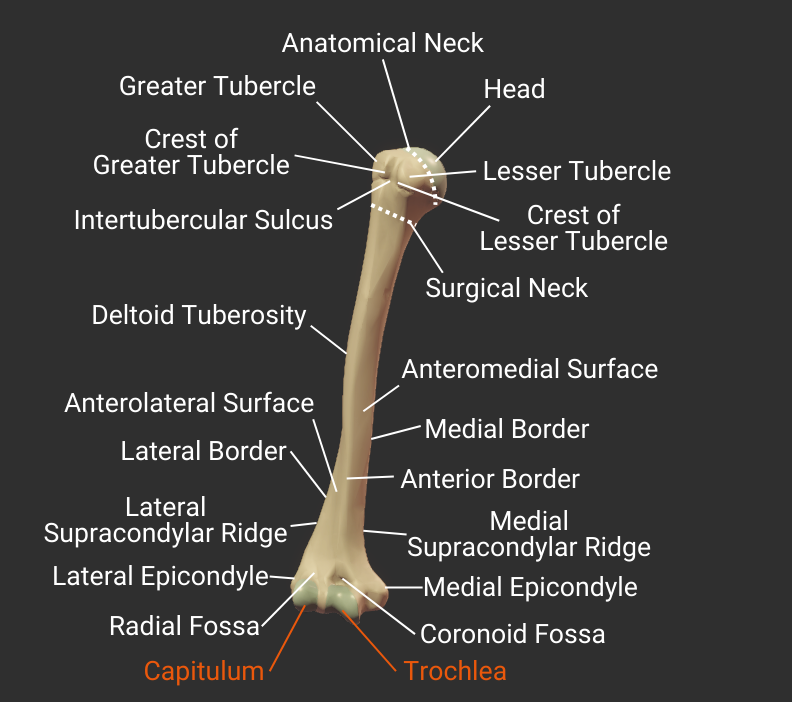
Head and Neck
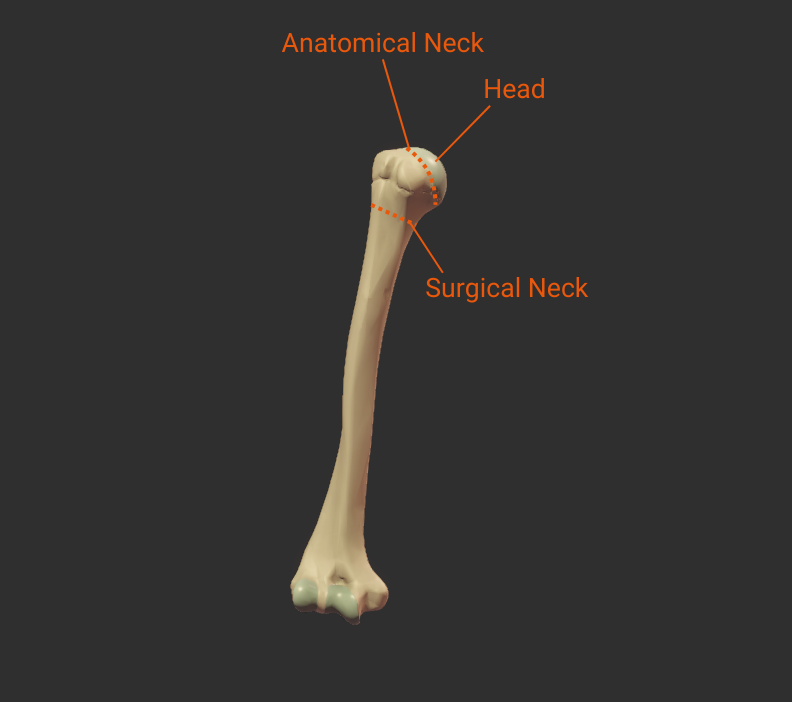
Click the bulleted names for more information.
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
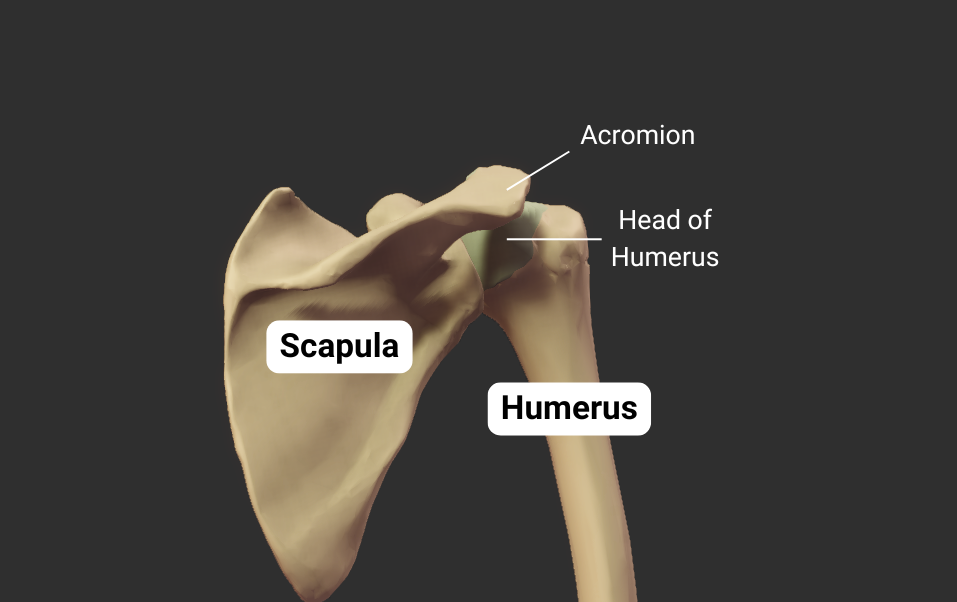
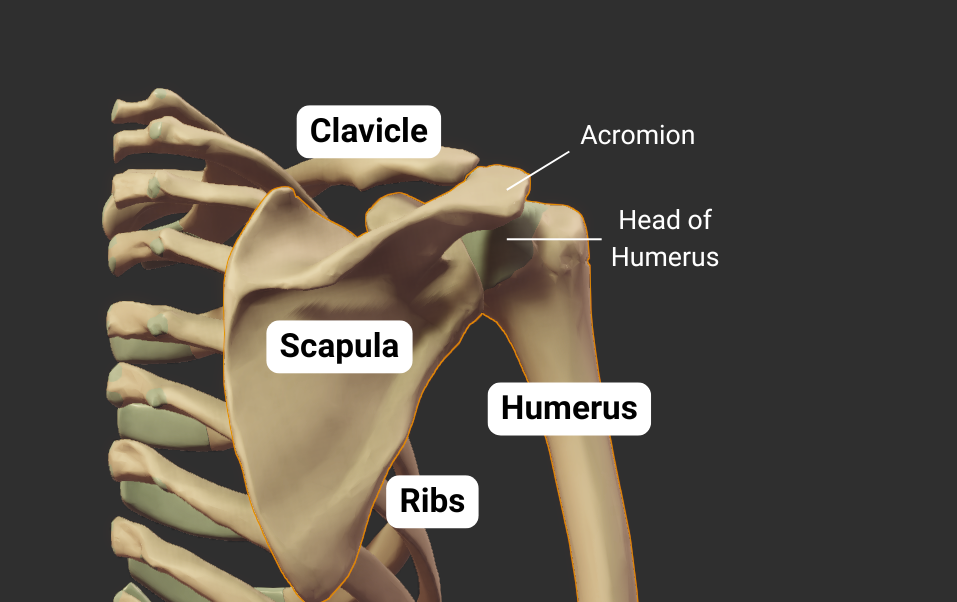
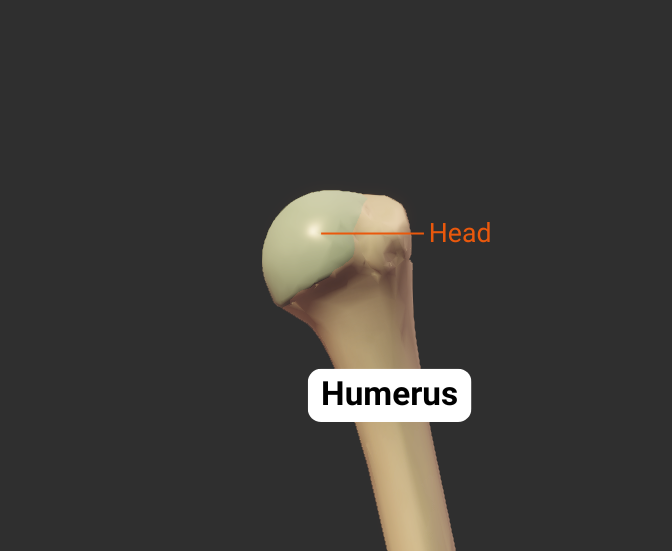
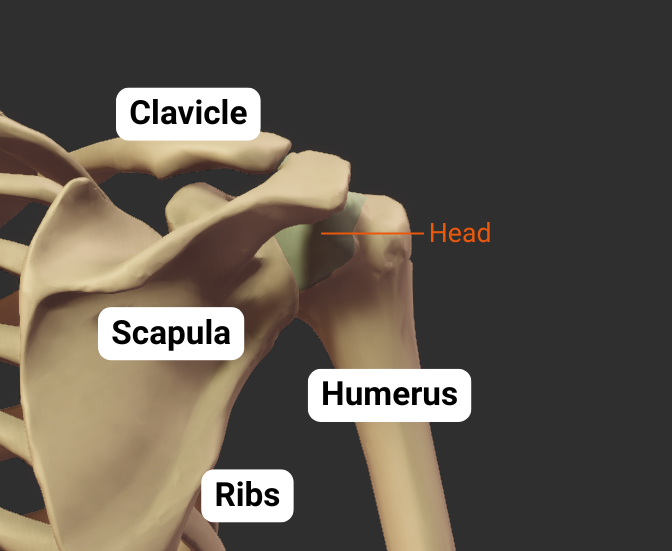
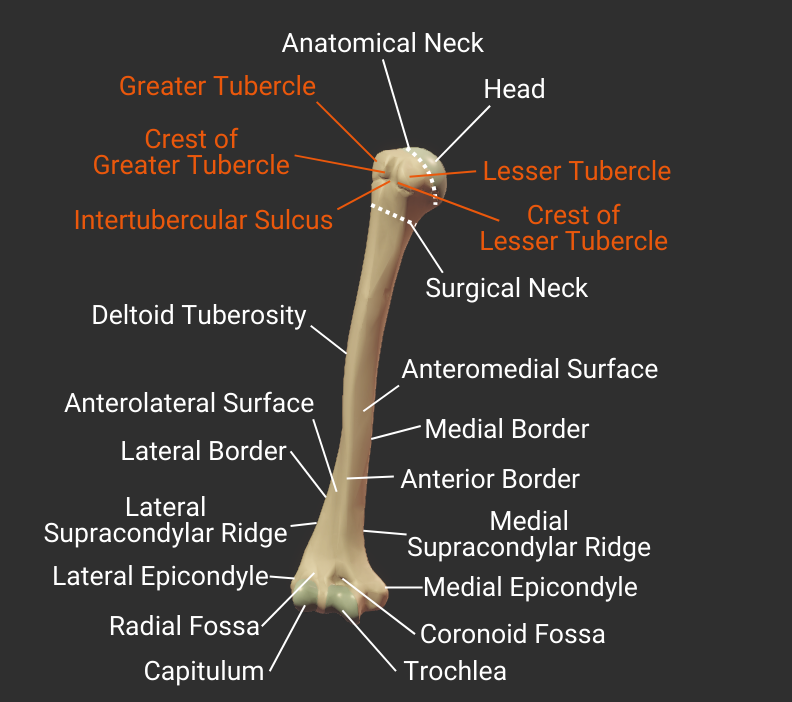
Head
- Articulates with glenoid fossa of scapula to form the shoulder (glenohumeral) joint
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
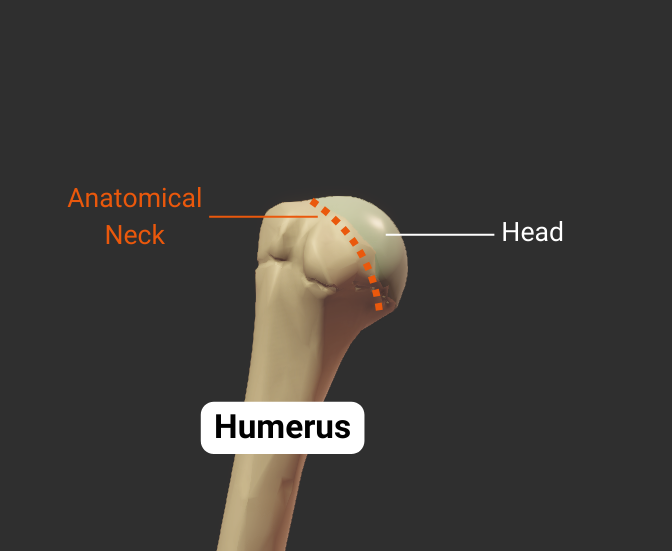
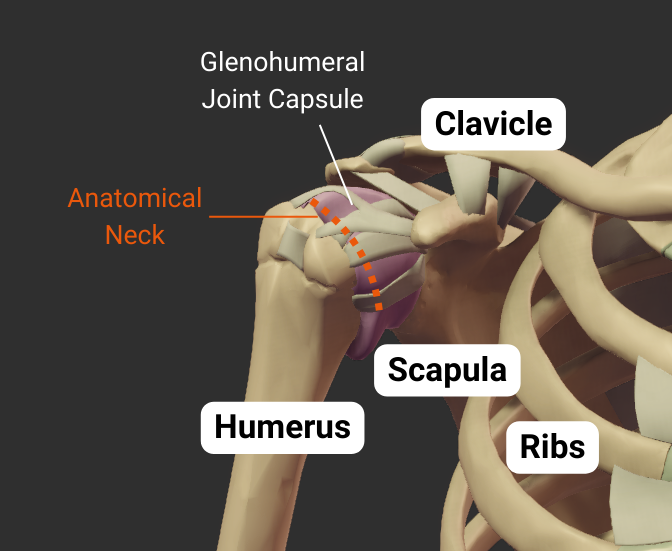
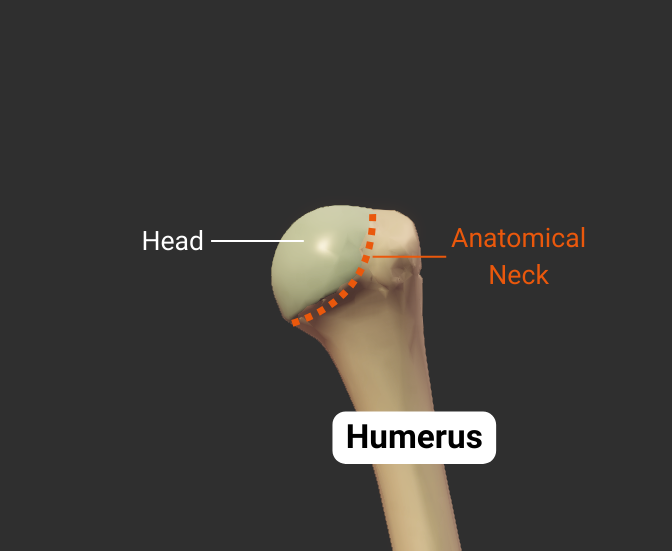
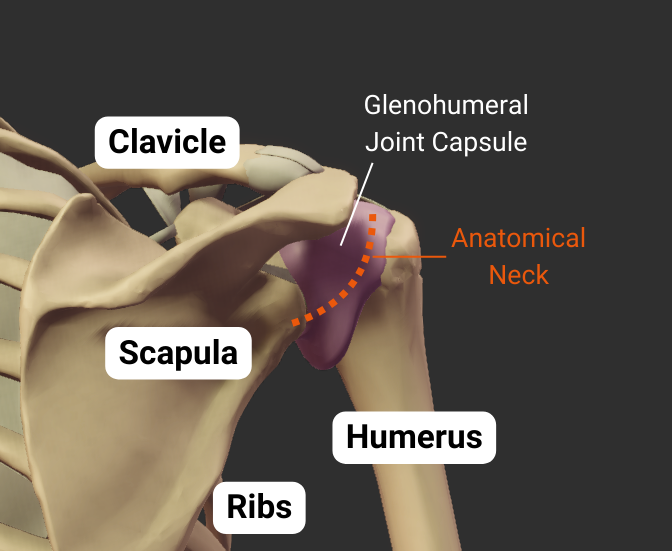
Anatomical Neck
- Narrow region distal to the humerus's head
- Attachment site for the glenohumeral joint's capsule
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
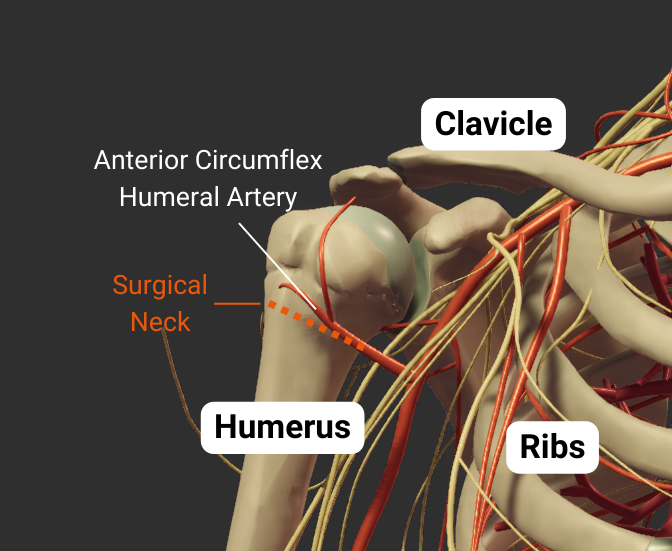
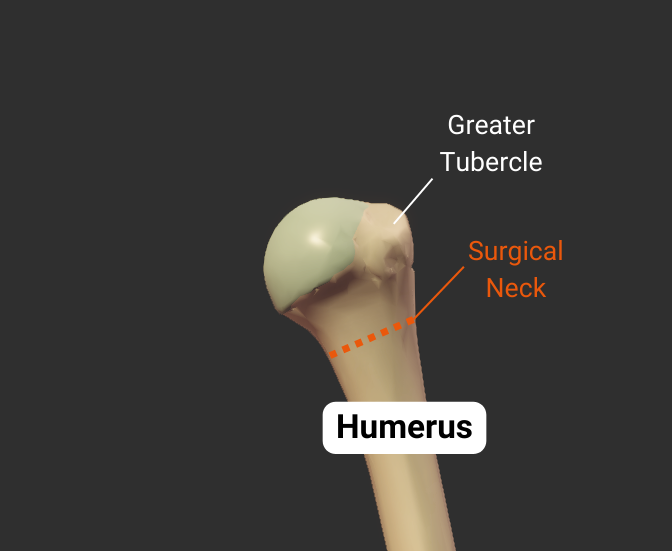
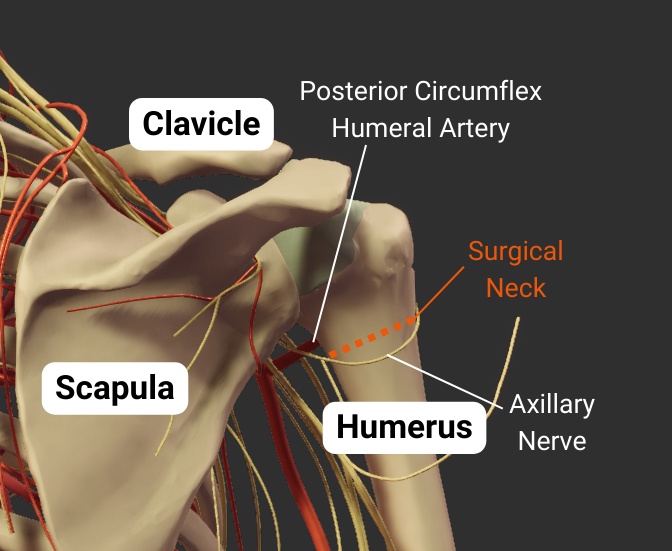
Surgical Neck
- Narrow region distal to tubercles
- Common fracture site
- Close to axillary nerve, anterior circumflex humeral artery, and posterior circumflex humeral artery
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
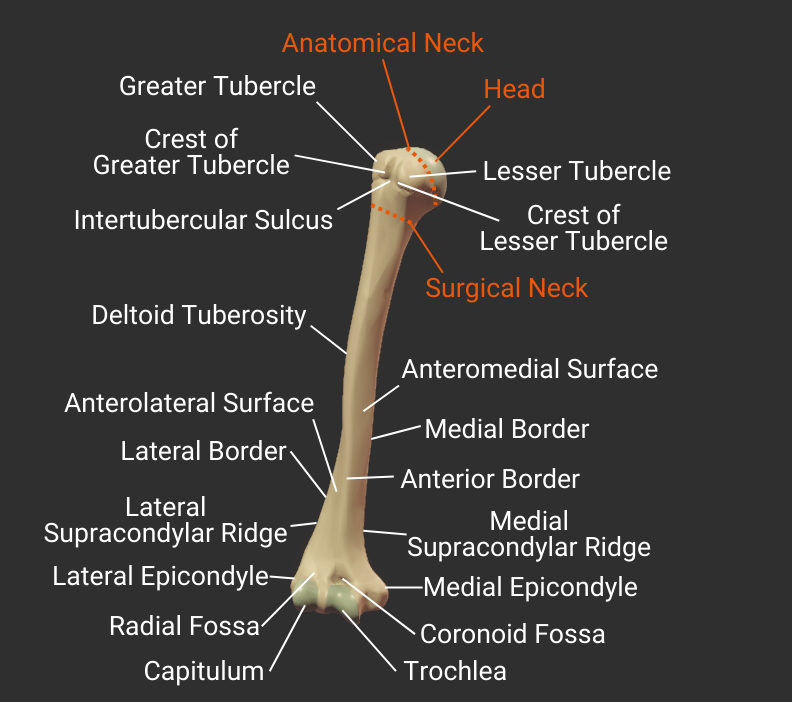
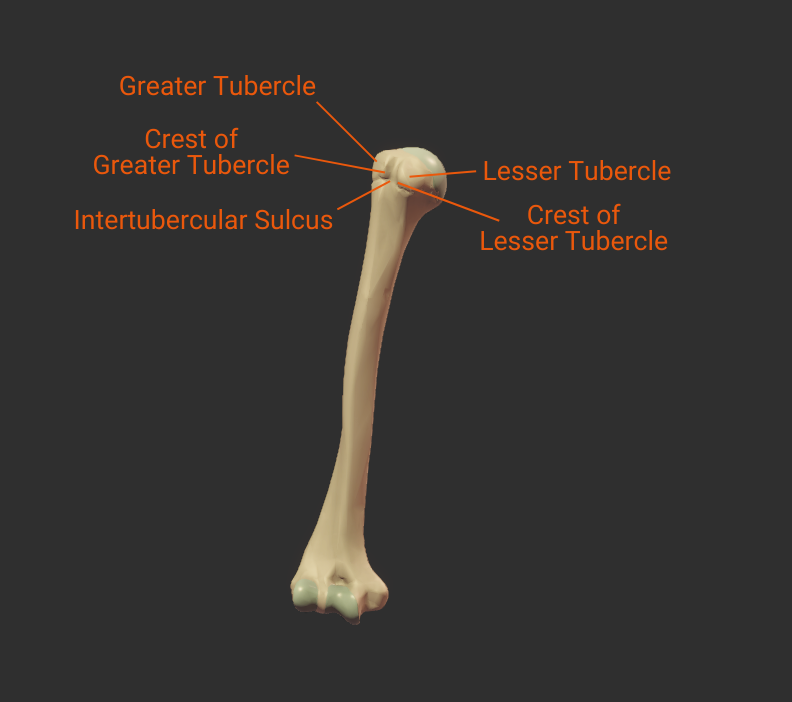
Tubercles
Click the bulleted names for more information.
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
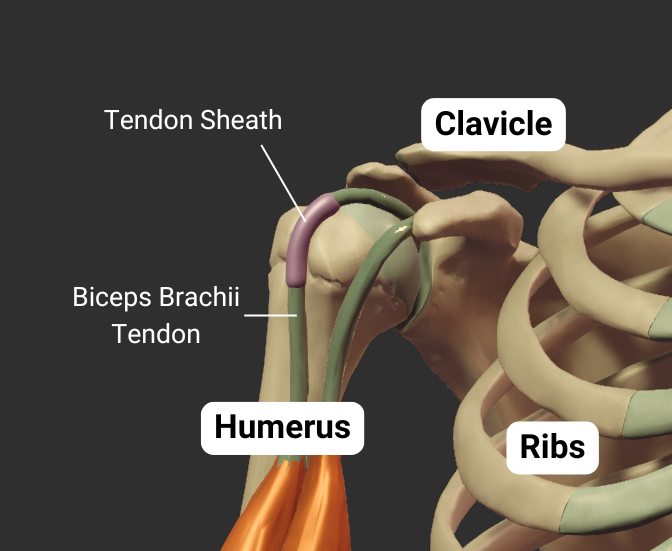
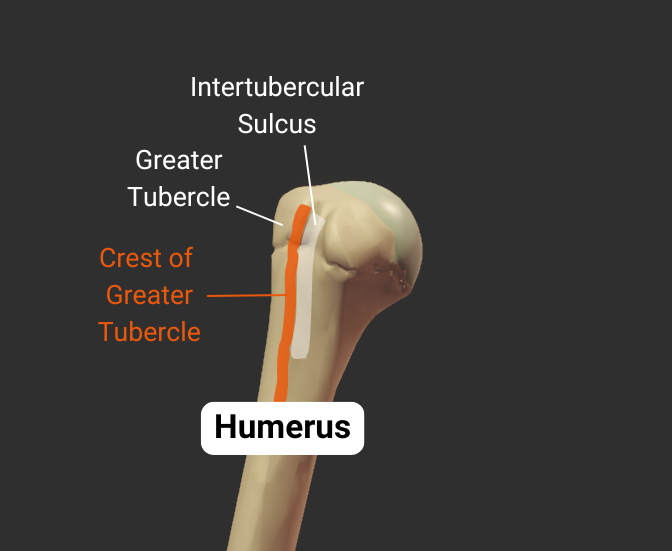
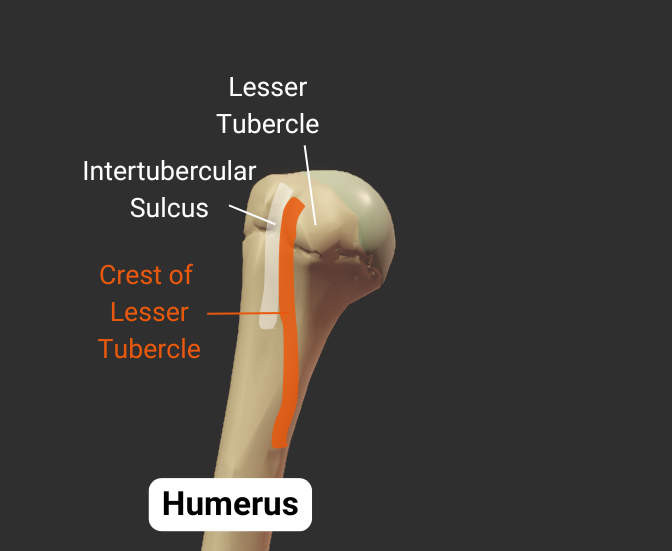
Intertubercular Sulcus
- Groove between the greater and lesser tubercles
- Guides the long tendon of the biceps brachii
- Also called the bicipital groove due to its relation with the biceps brachii tendon
- Insertion site for the latissimus dorsi
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
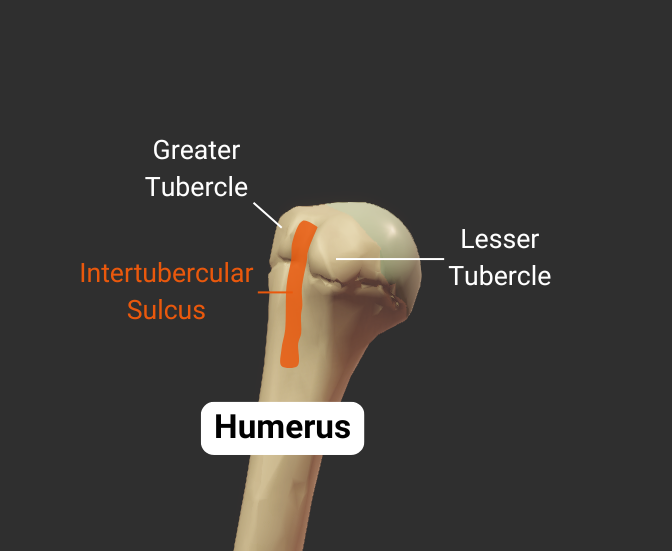
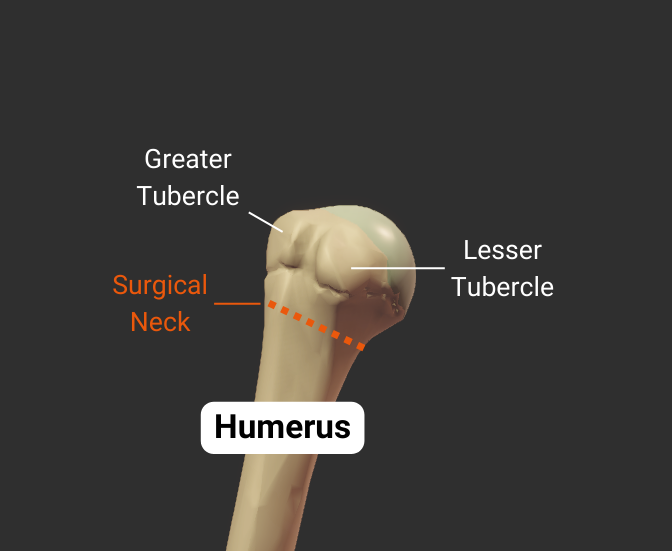
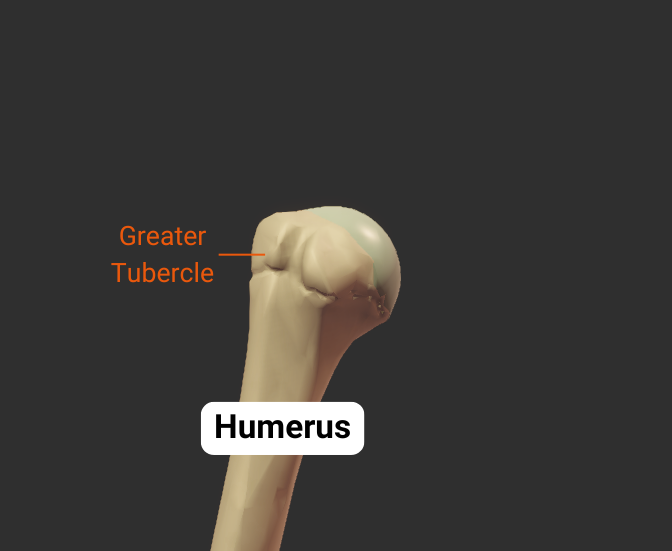
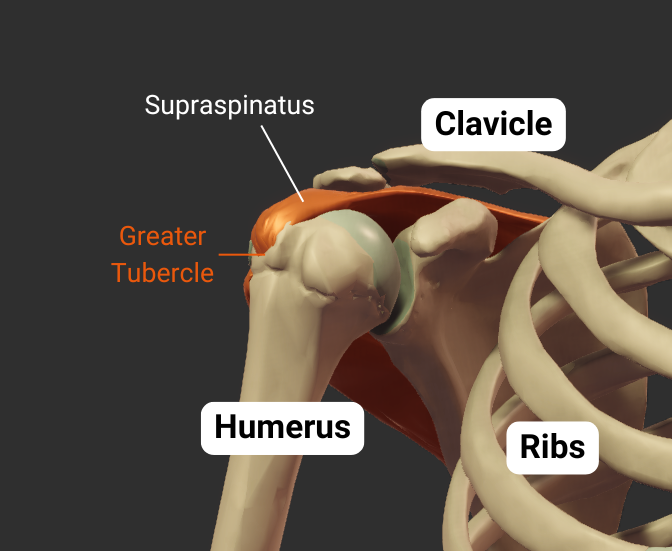
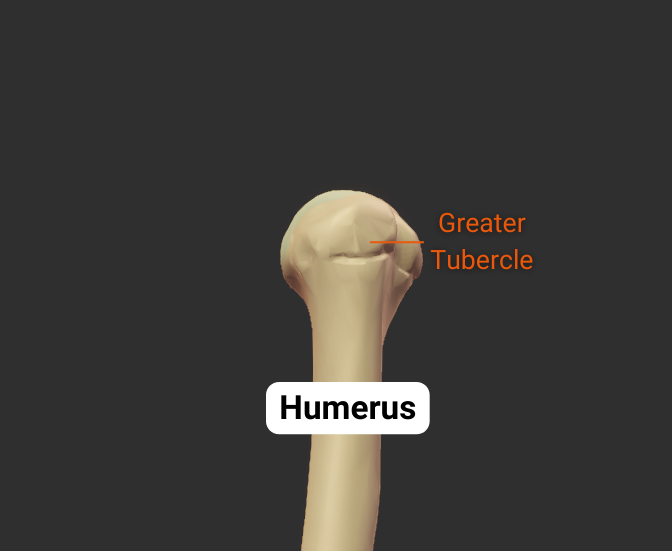
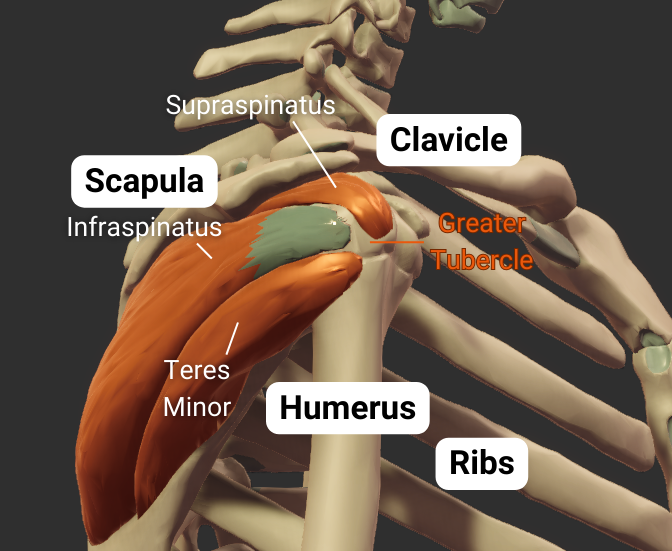
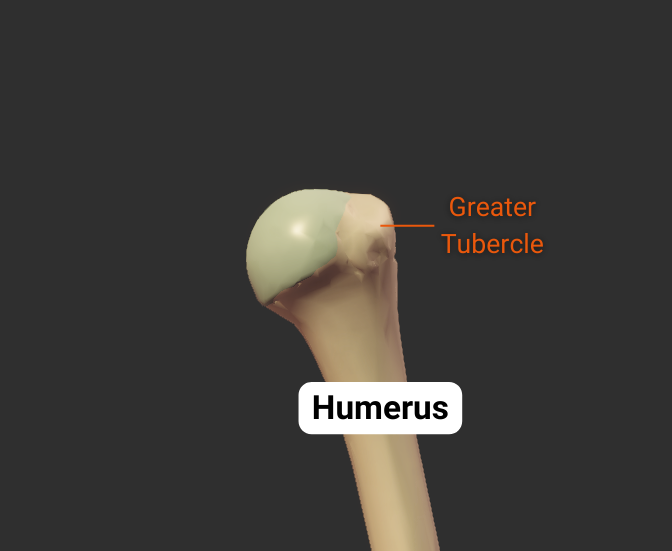
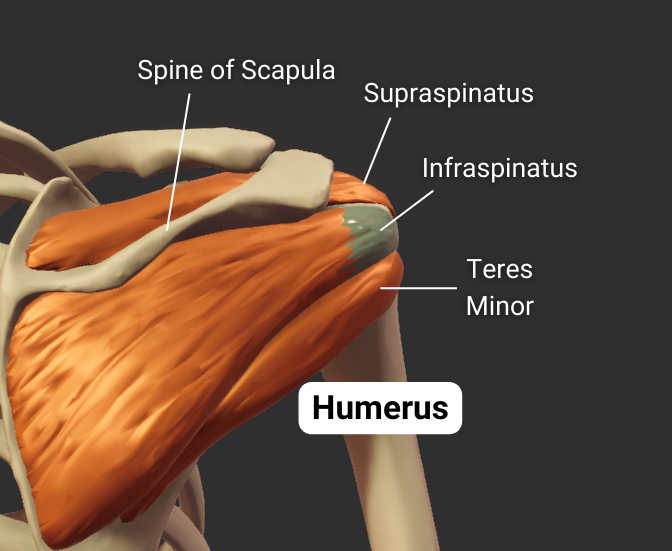
Greater Tubercle
- Lateral projection between the anatomical and surgical necks
- Insertion site for supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor (rotator cuff muscles)
- Covered by the deltoid to form a person's rounded shoulder
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
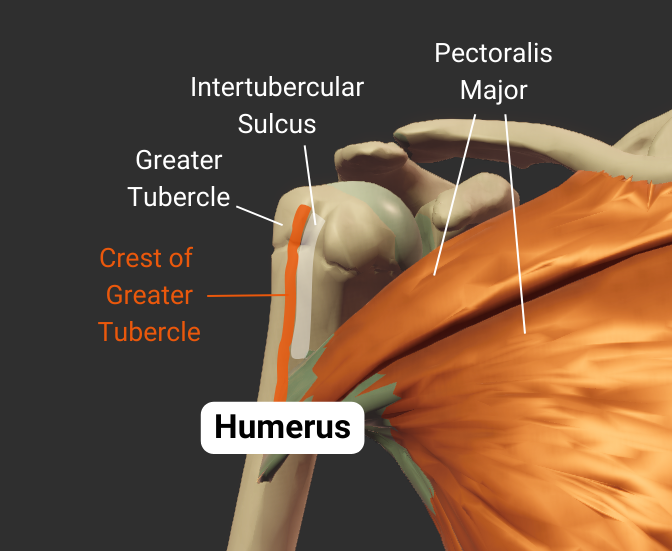
Crest of Greater Tubercle
- Lateral lip of the intertubercular sulcus
- Insertion site for the pectoralis major's tendon
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
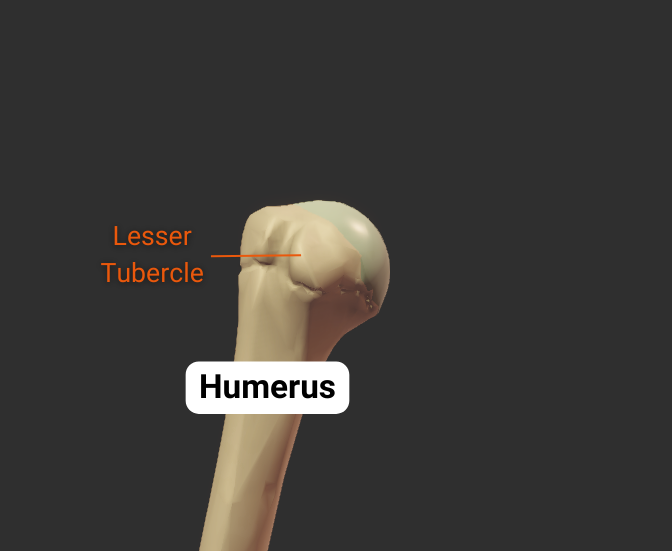
Lesser Tubercle
- Anterior projection between the anatomical and surgical necks
- Insertion site for the subscapularis (rotator cuff muscle)
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
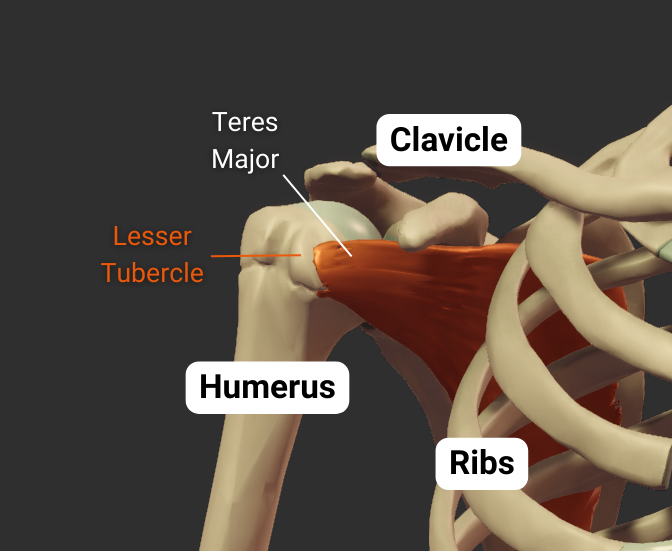
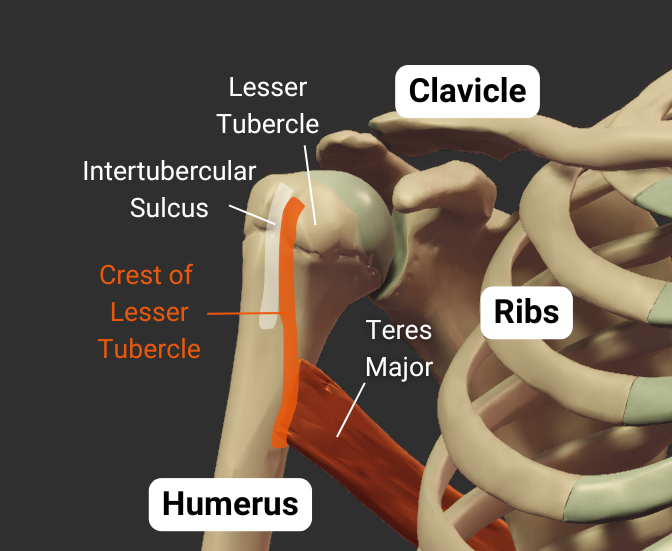
Crest of Lesser Tubercle
- Medial lip of the intertubercular sulcus
- Insertion site for the teres major's tendon
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
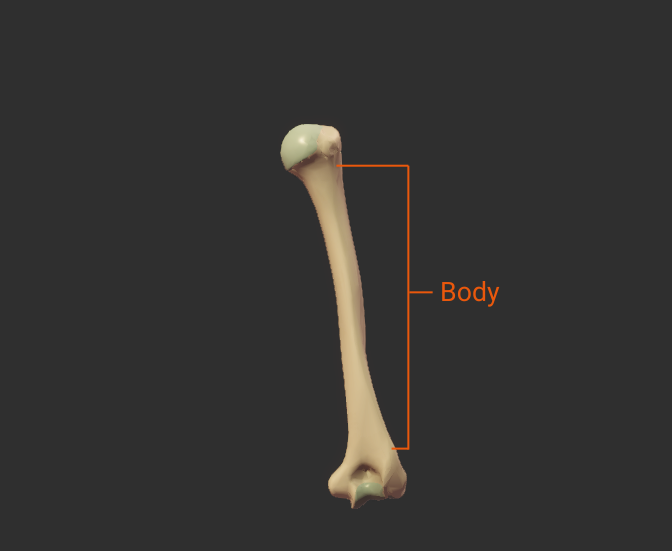
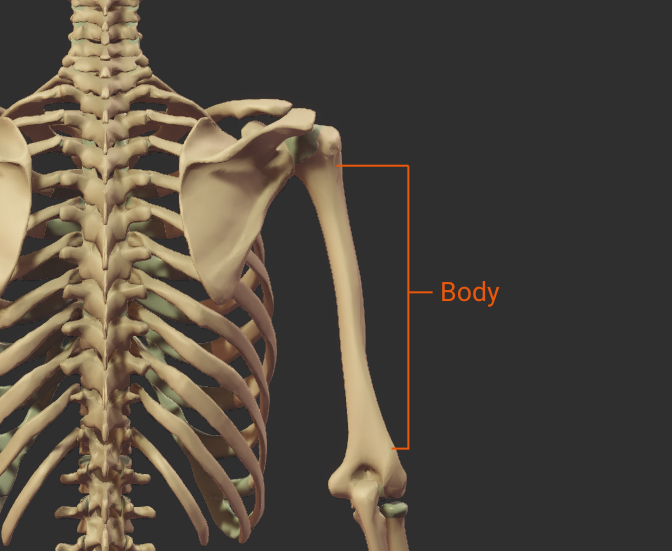
Body
Click the bulleted names for more information.
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
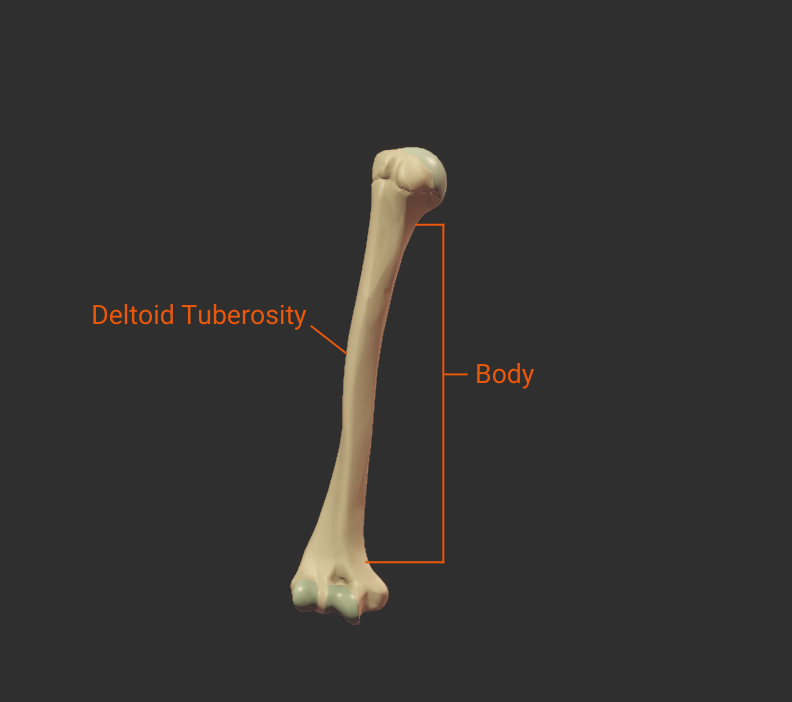
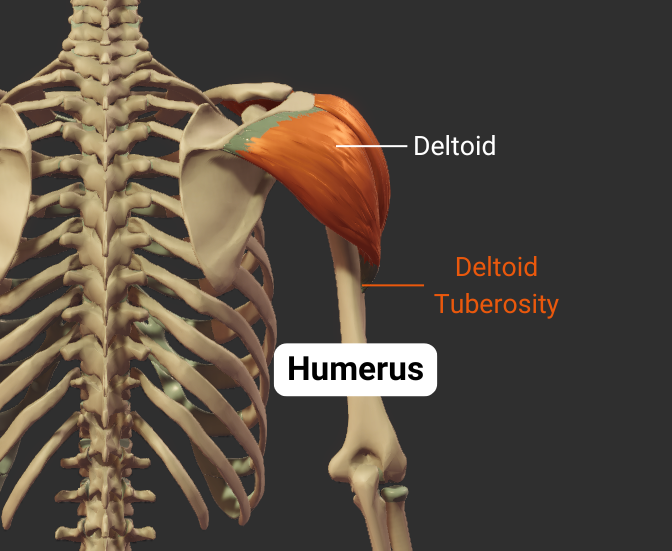
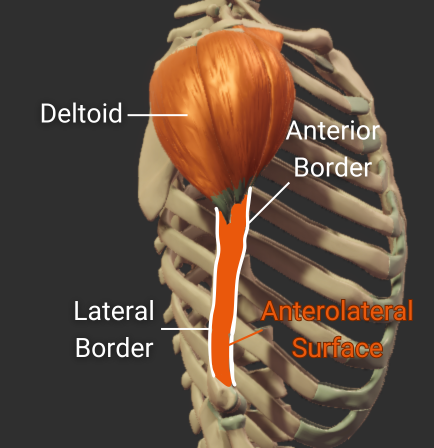
Deltoid Tuberosity
- Rough lateral region in the middle of humerus
- Insertion site for the deltoid
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
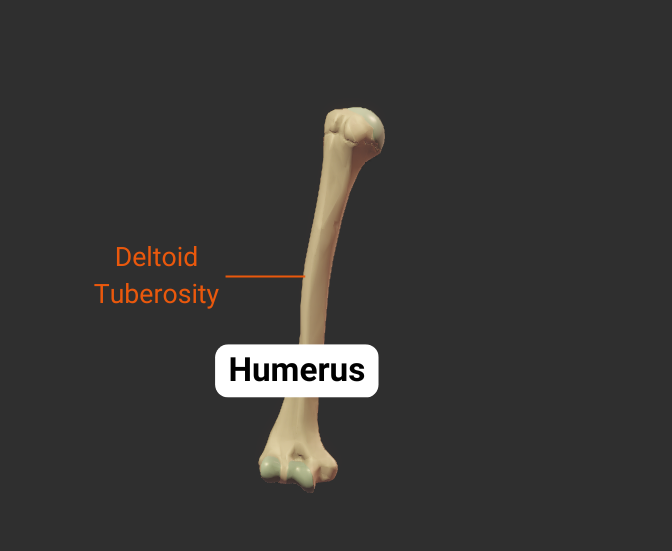
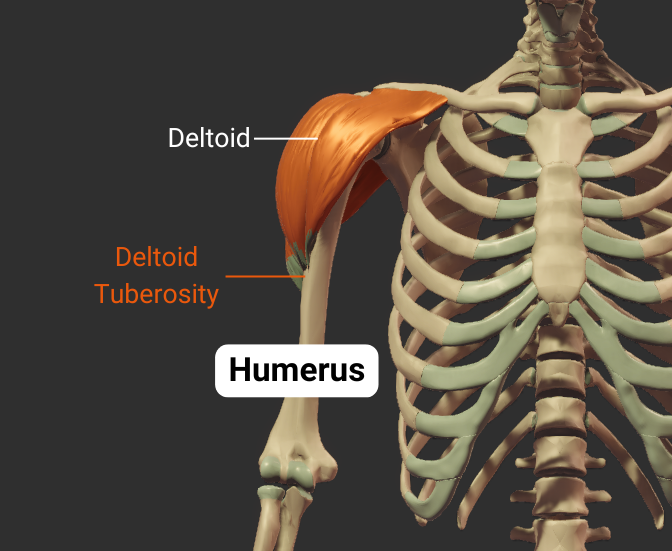
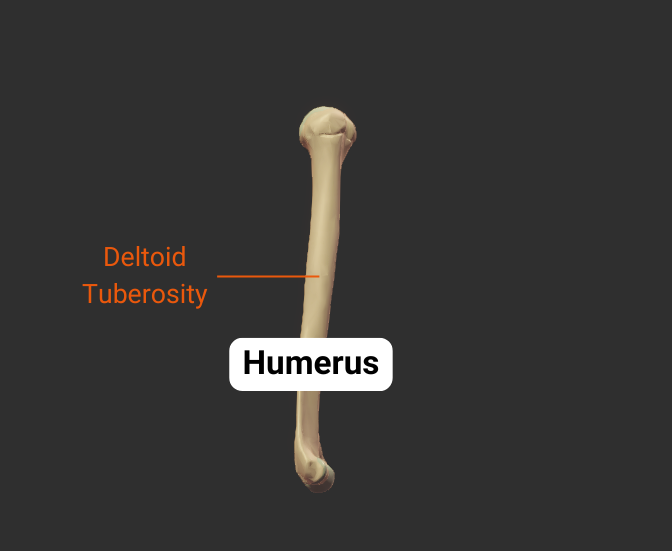
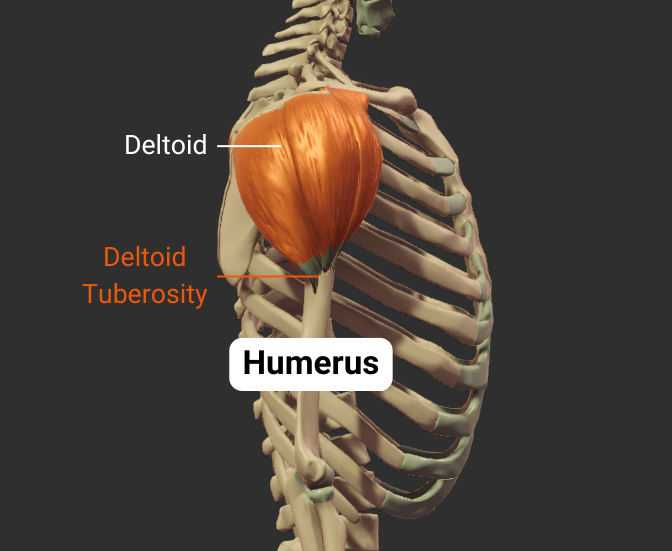
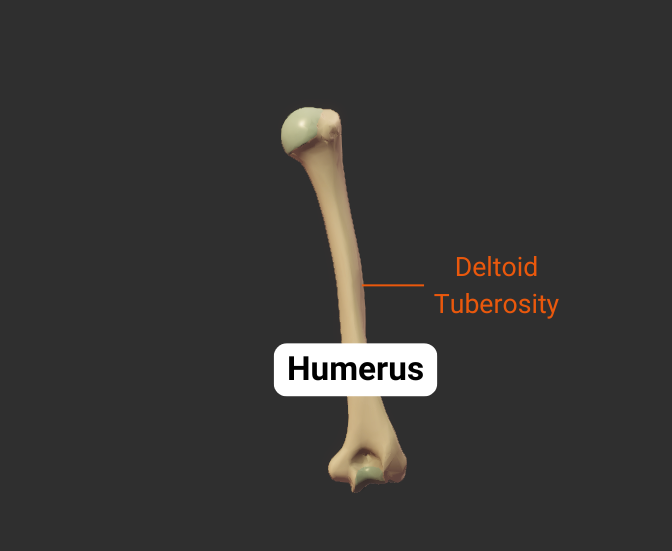
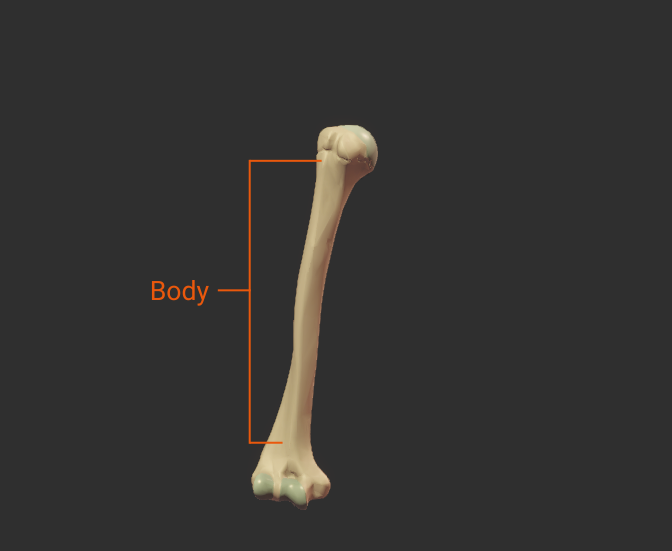
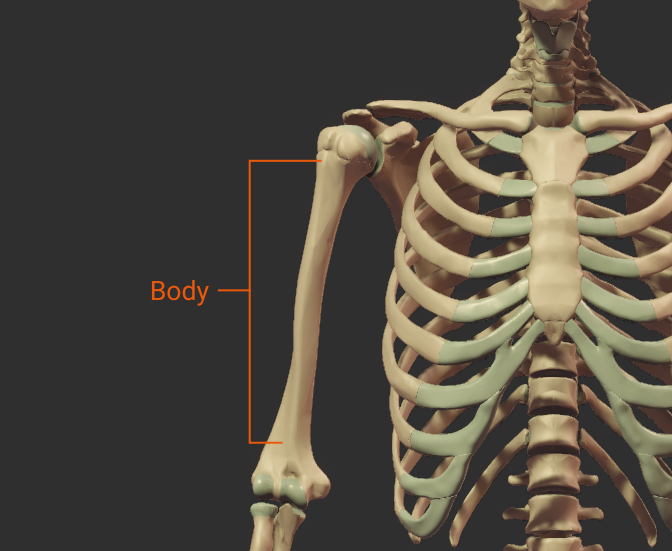
Body
- The shaft of the humerus (the bone's long midsection)
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
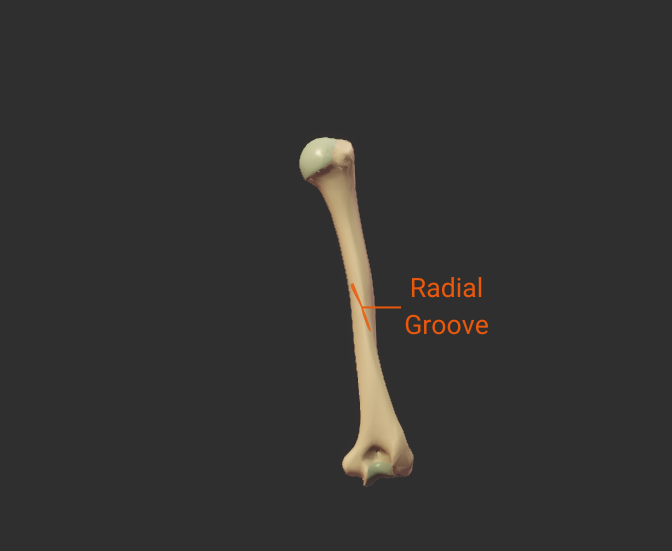
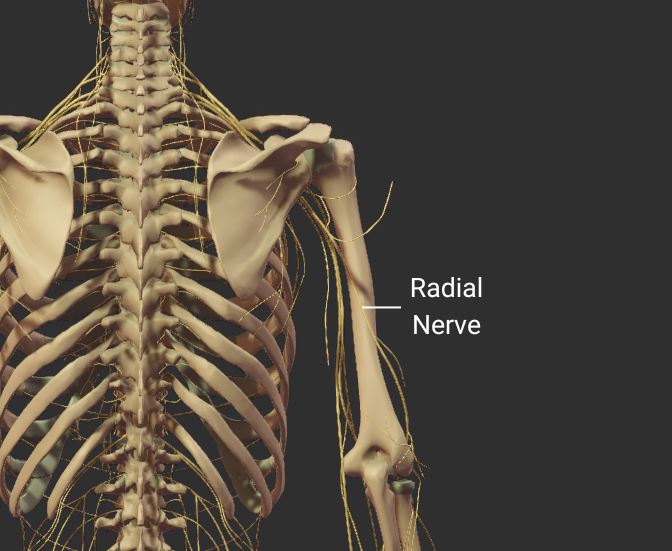
Radial Groove
- Spiral groove on the shaft's posterior surface
- Guides the radial nerve and deep brachial artery
- Fractures here risk nerve injury
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
Borders
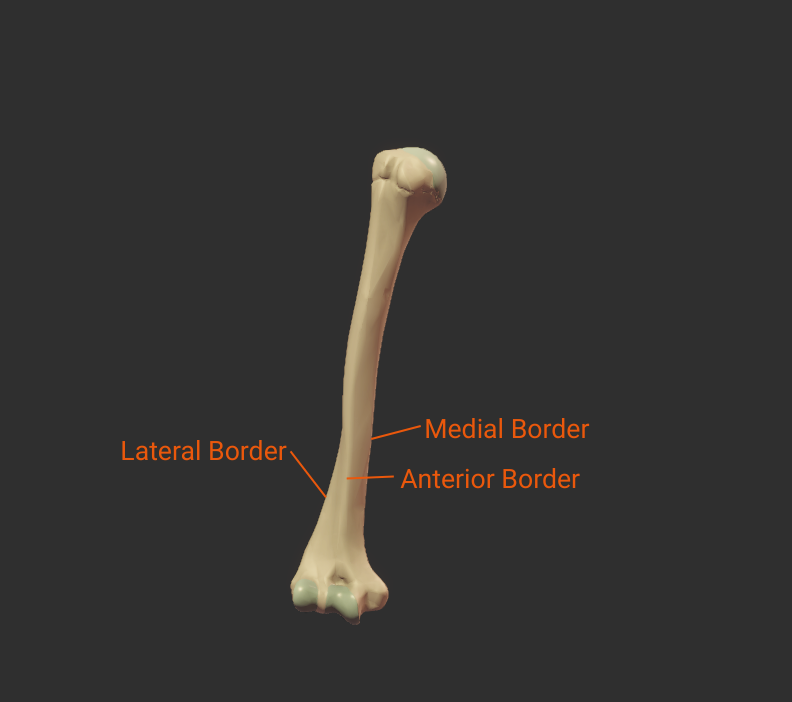
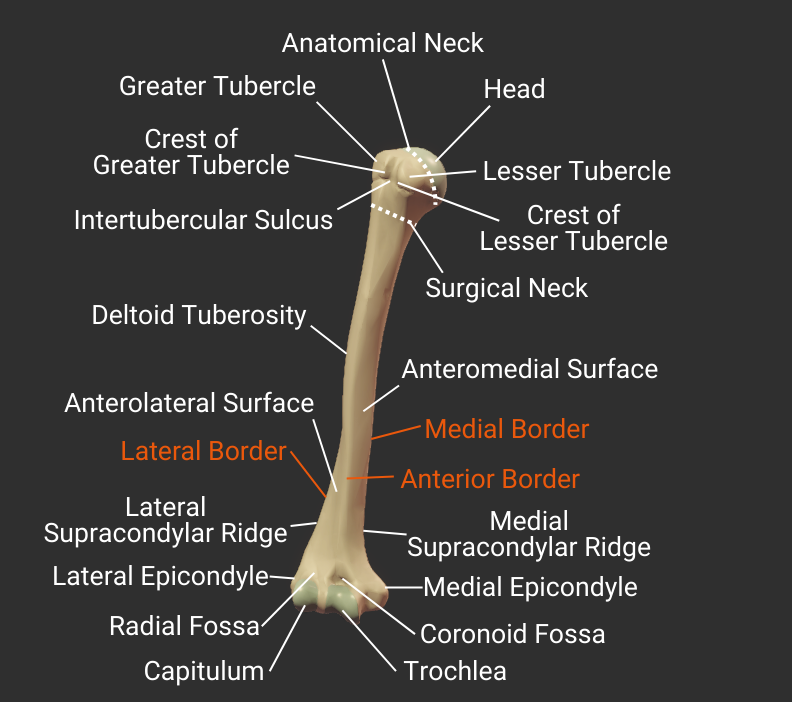
Click the bulleted names for more information.
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
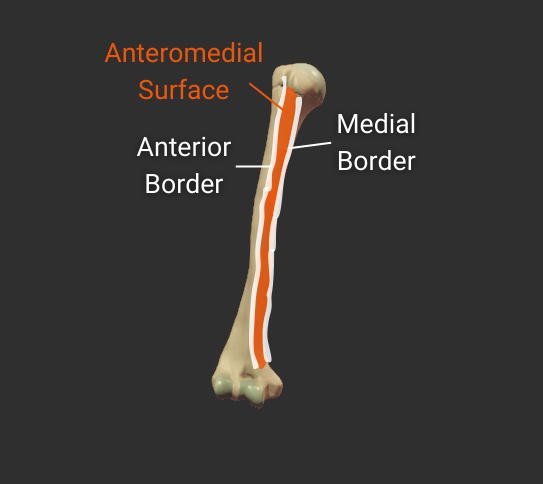
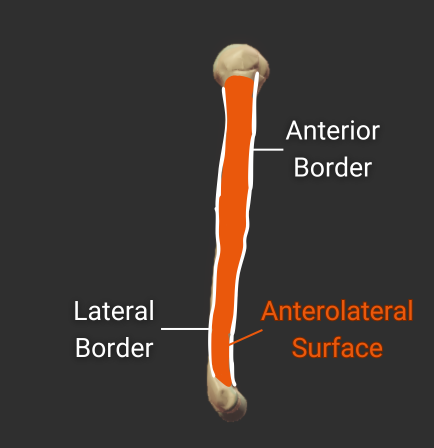
Anterior Border
- Anterior ridge on the humerus's body
- Proximal end is the crest of the greater tubercle
- Separates the anteromedial and anterolateral surfaces
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
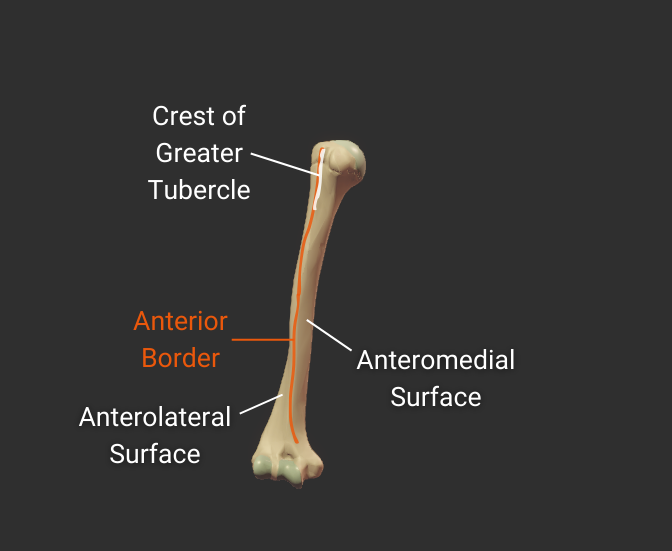
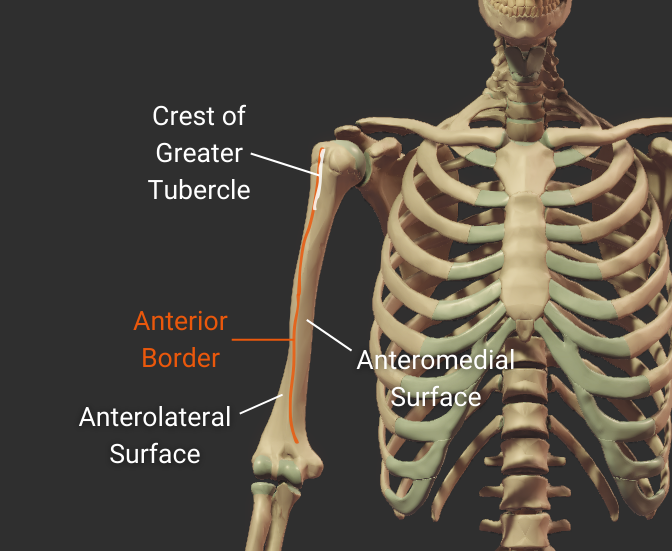
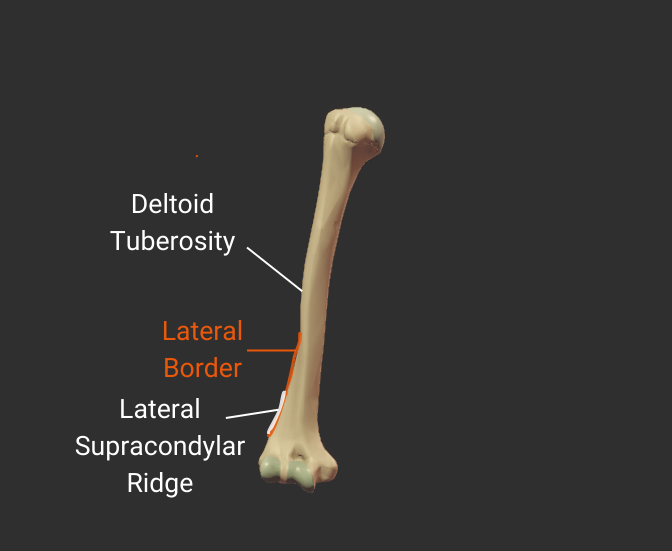
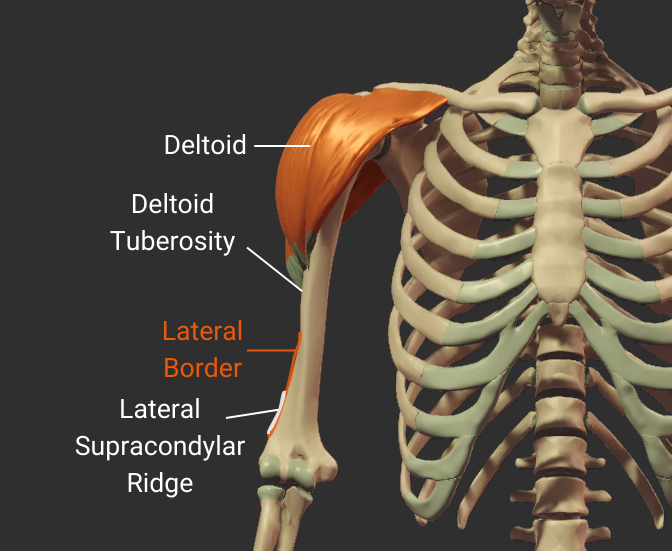
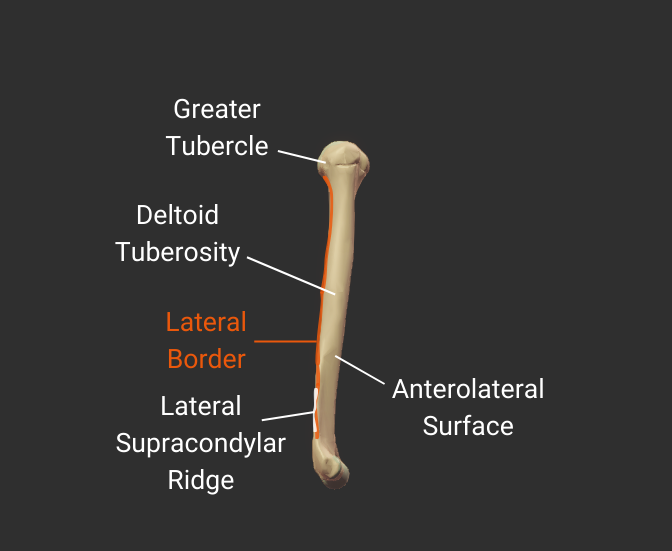
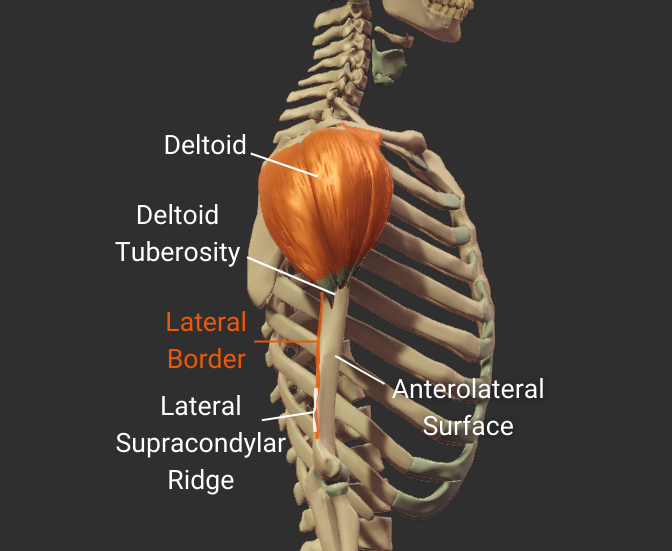
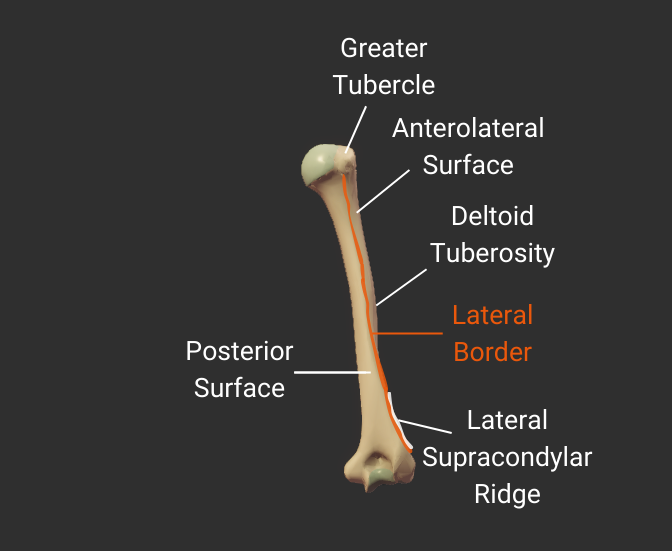
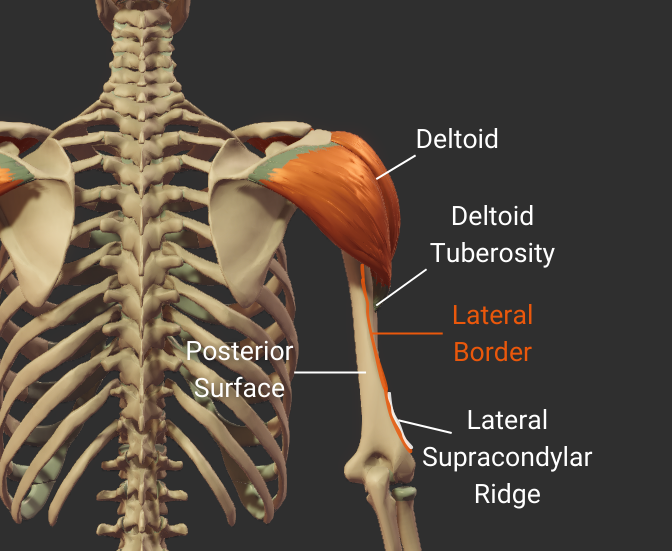
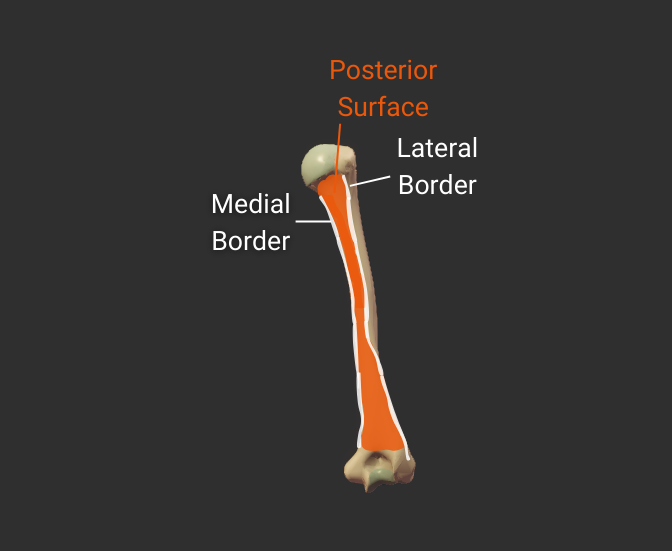
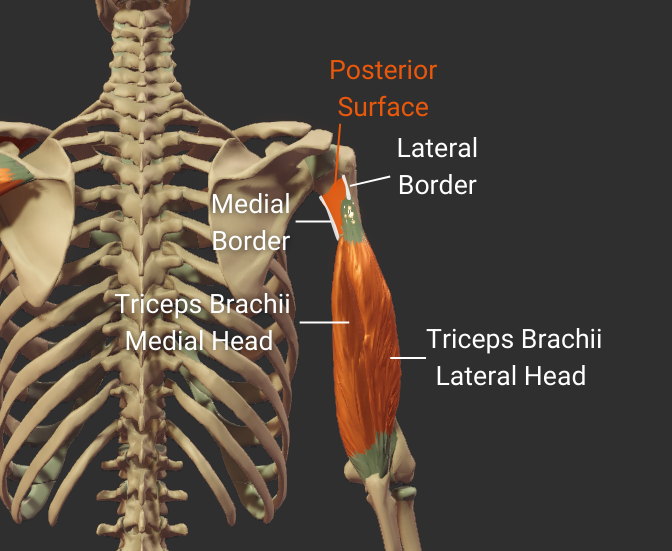
Lateral Border
- Lateral ridge on the humerus's body
- Starts at the greater tubercle
- Runs next to the deltoid tuberosity
- Distal end is the lateral supracondylar ridge
- Separates the anterolateral and posterior surfaces
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
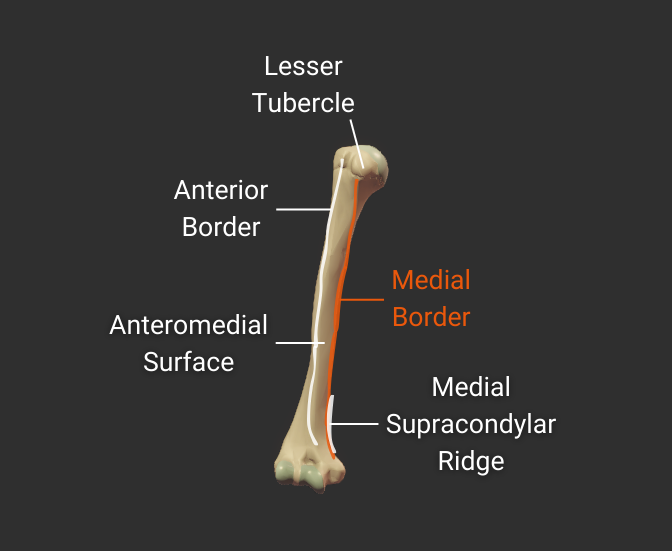
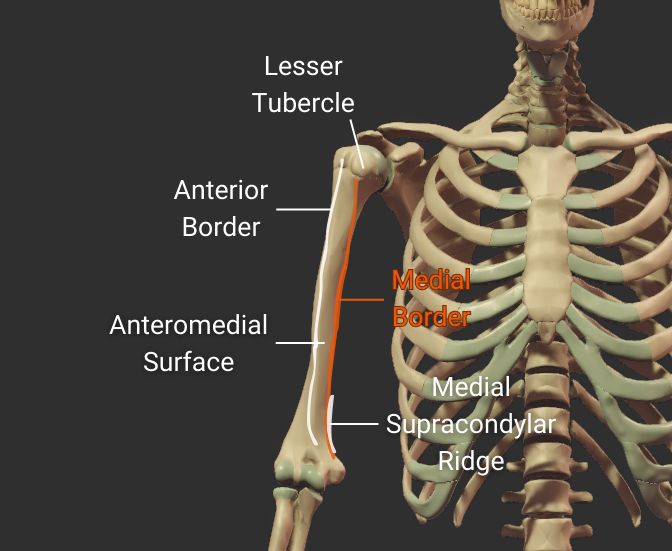
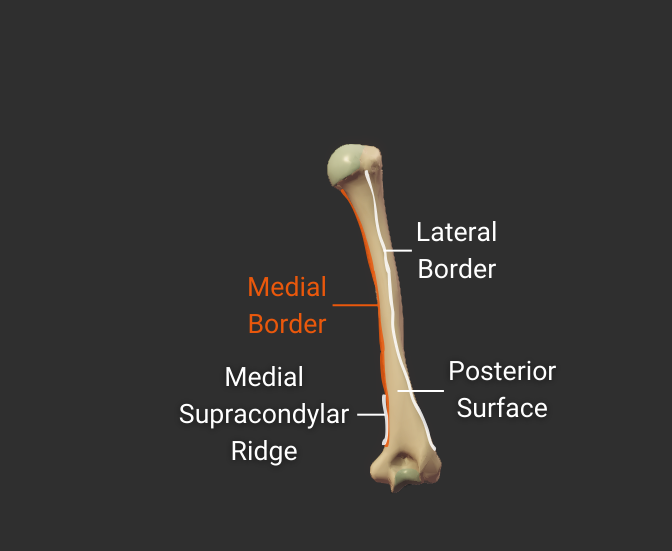
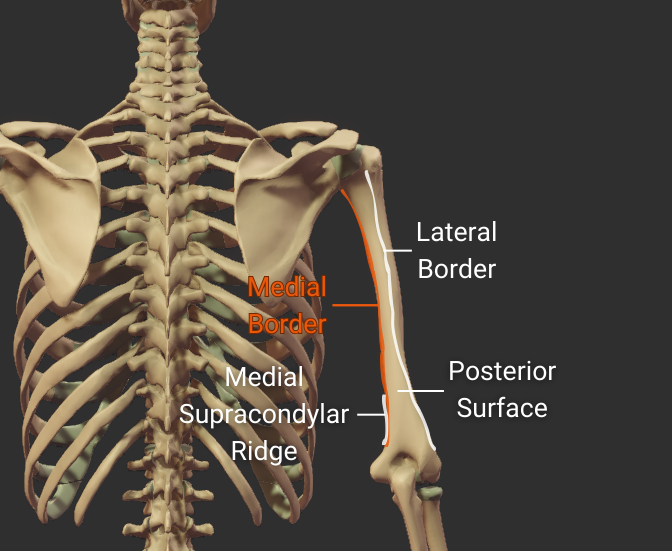
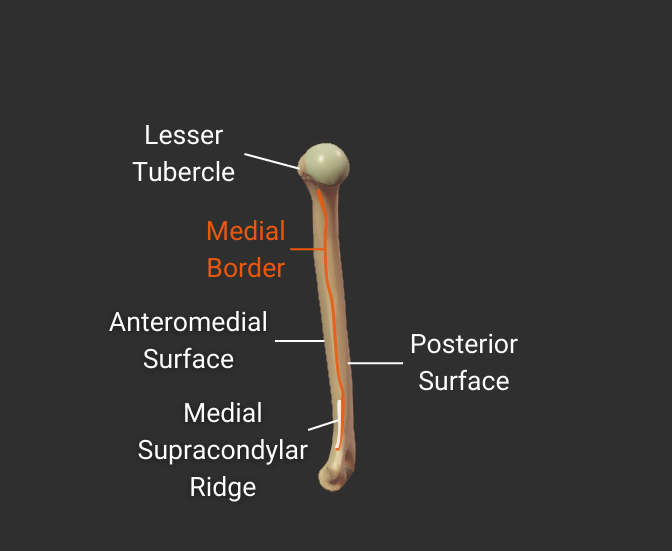
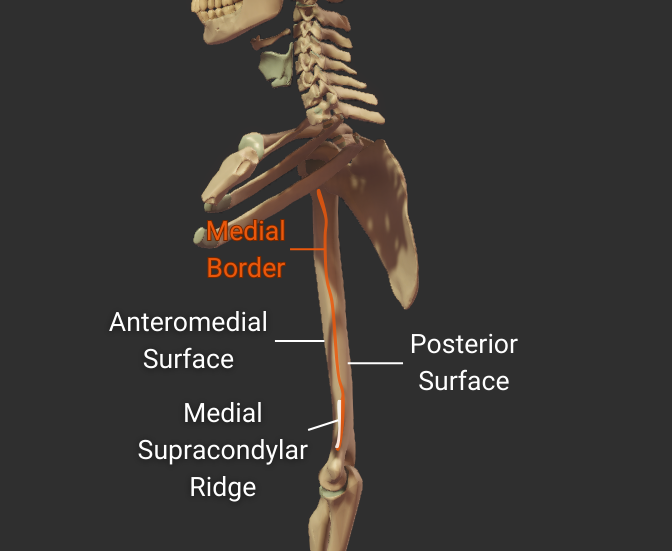
Medial Border
- Medial ridge on the humerus's body
- Starts at the lesser tubercle
- Distal end is the medial supracondylar ridge
- Separates the anteromedial and posterior surfaces
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
Surfaces
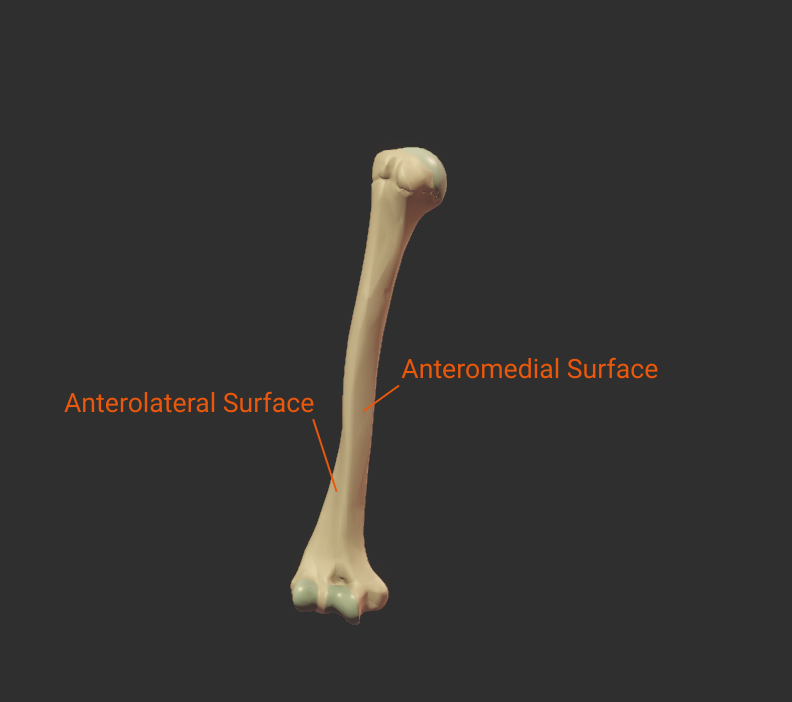
Click the bulleted names for more information.
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
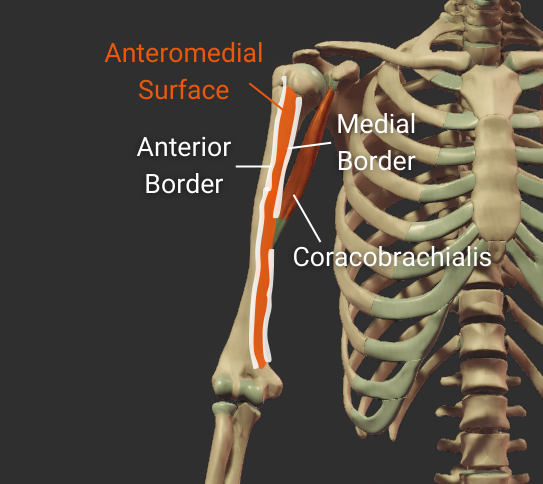
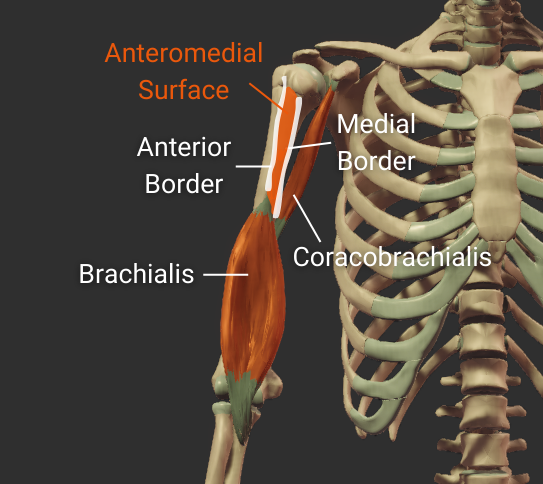
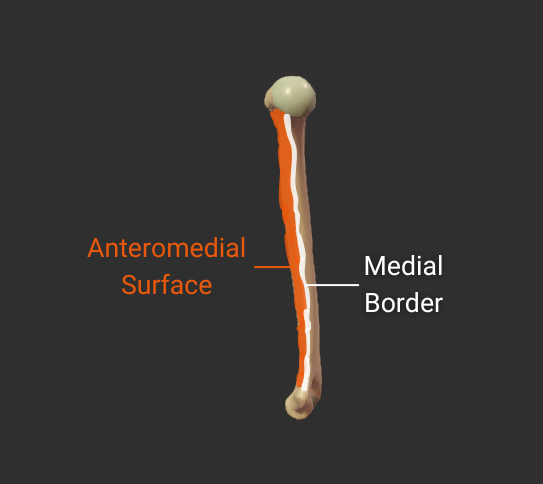
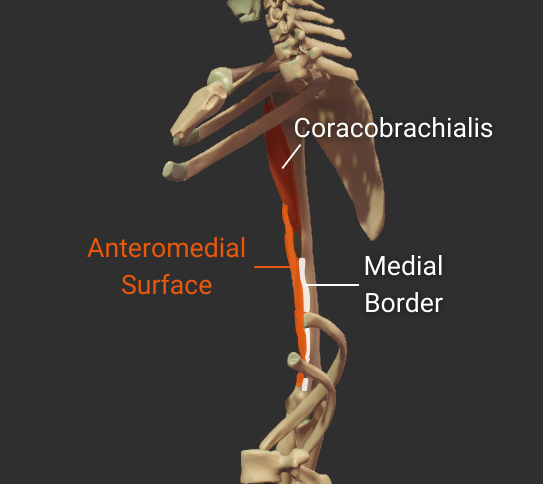
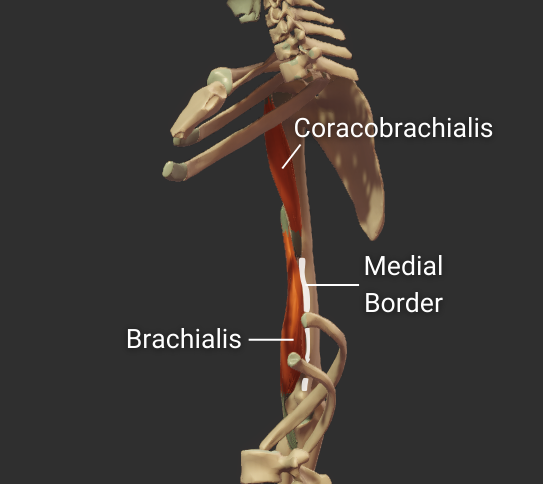
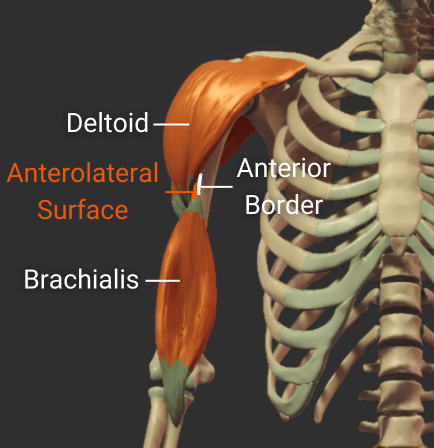
Anteromedial Surface
- Surface between the anterior and medial borders
- Encompasses the intertubercular groove
- Distal portion is covered by the brachialis
- Insertion site for the coracobrachialis
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
Anterolateral Surface
- Surface between the anterior and lateral borders"
- Encompasses the deltoid tuberosity
- Proximal portion is covered by the deltoid
- Origin site for the lateral brachialis
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
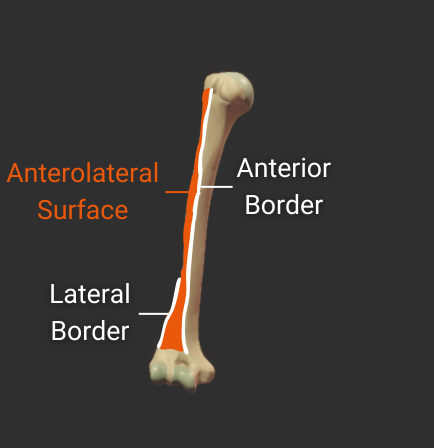
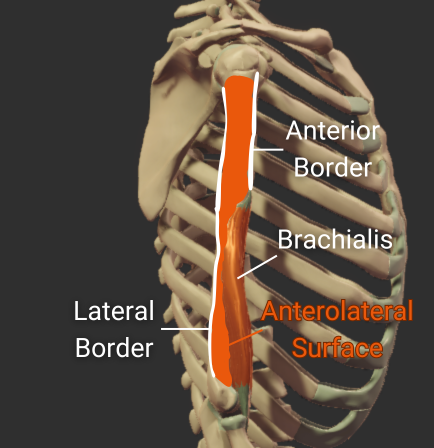
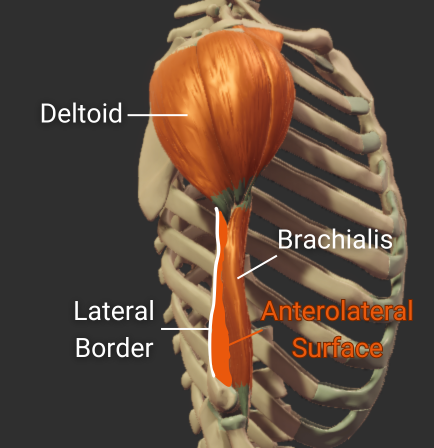
Posterior Surface
- Surface between the lateral and medial borders
- Covered by the medial head of the triceps brachii
-
Origin site for the medial and lateral heads of the triceps
- Medial head inserts inferior to the radial groove
- Lateral head inserts superior to the radial groove
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
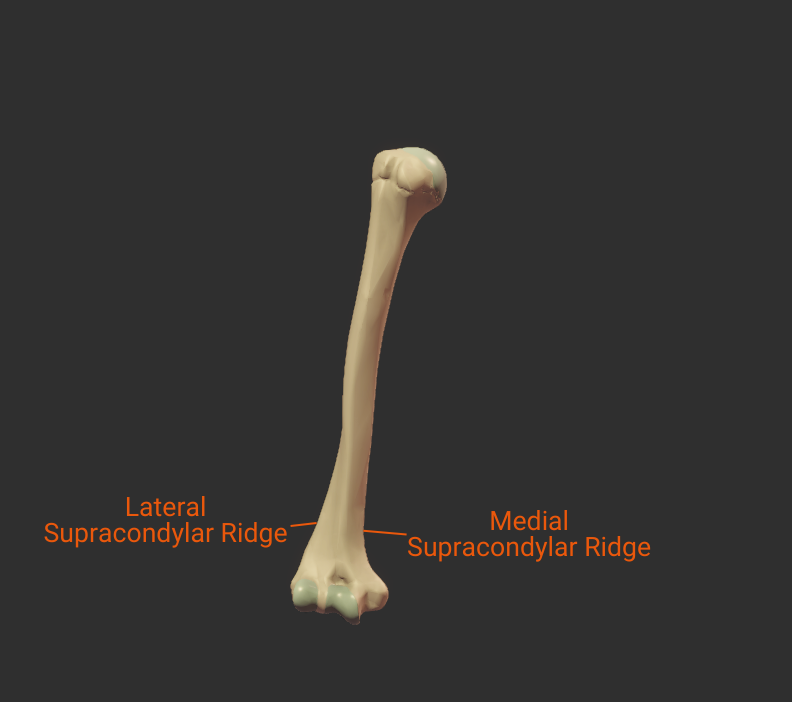
Supracondylar Ridges
Click the bulleted names for more information.
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
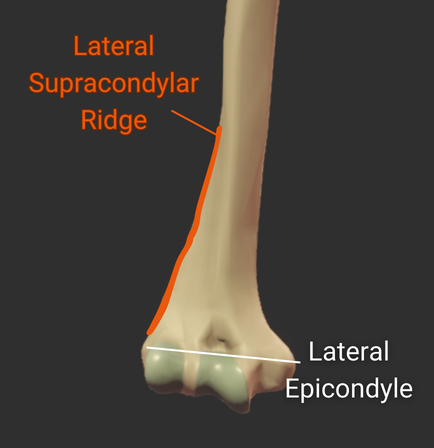
Lateral Supracondylar Ridge
- Ridge above the lateral epicondyle
- Origin site for the brachioradialis and the extensor carpi radialis longus
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
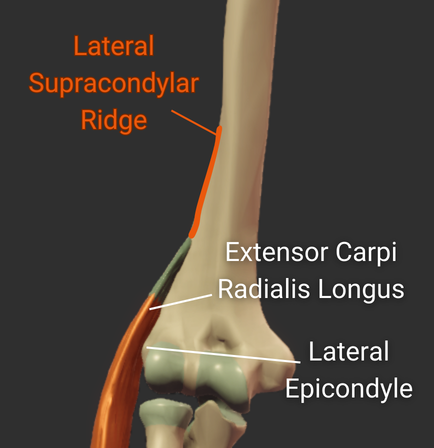
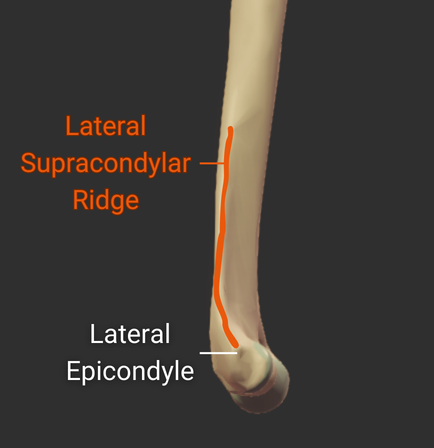
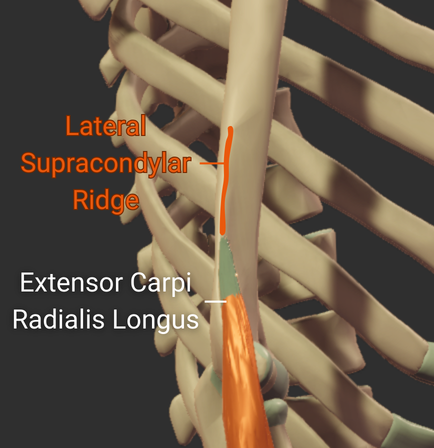
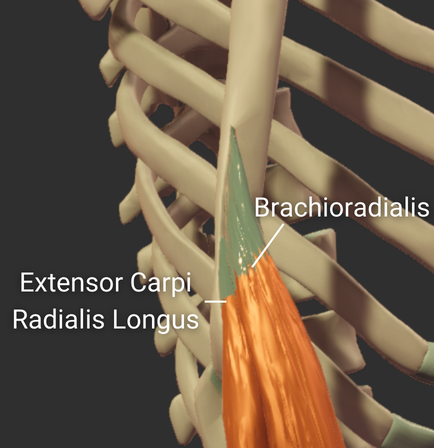
Medial Supracondylar Ridge
- Ridge above the medial epicondyle
- Origin site for the pronator teres's humeral head
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
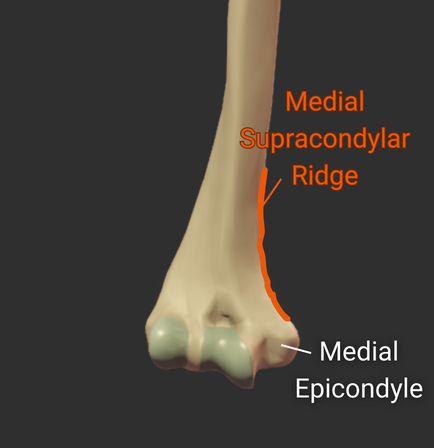
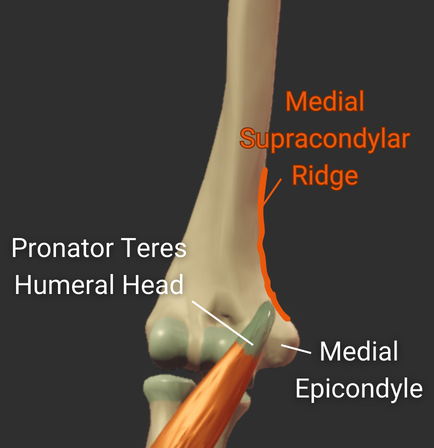
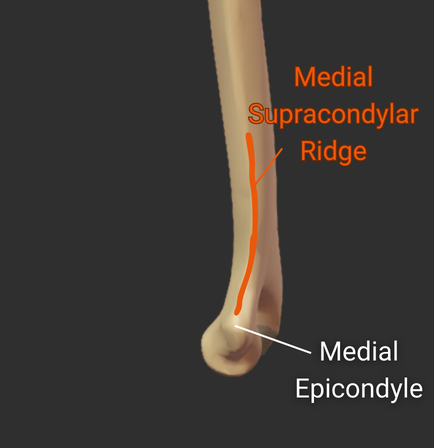
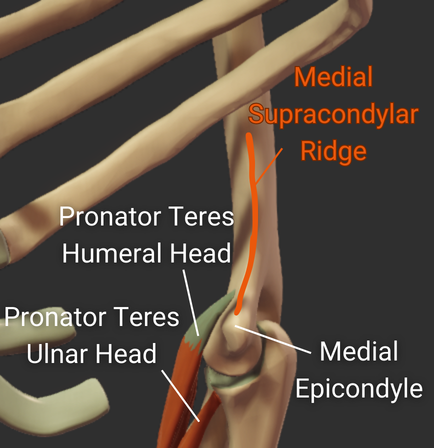
Epicondyles
Click the bulleted names for more information.
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
Lateral Epicondyle
- Small lateral prominence on the humerus's distal end
- Attachment site for the radial collateral ligament
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
Medial Epicondyle
- Larger medial prominence on the humerus's distal end
- Origin for forearm flexor muscles and ulnar collateral ligament
- The posterior side contains the groove for the ulnar nerve
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
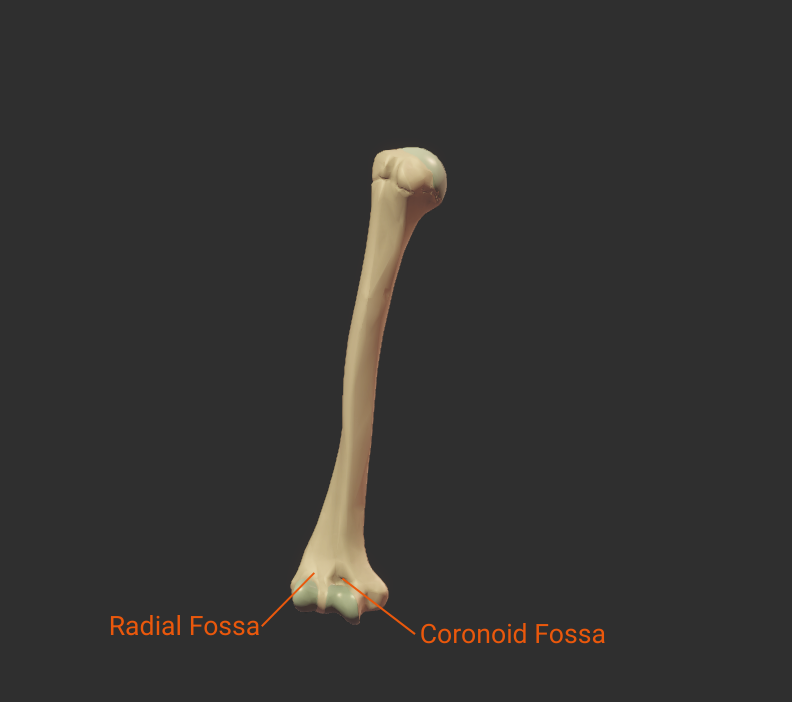
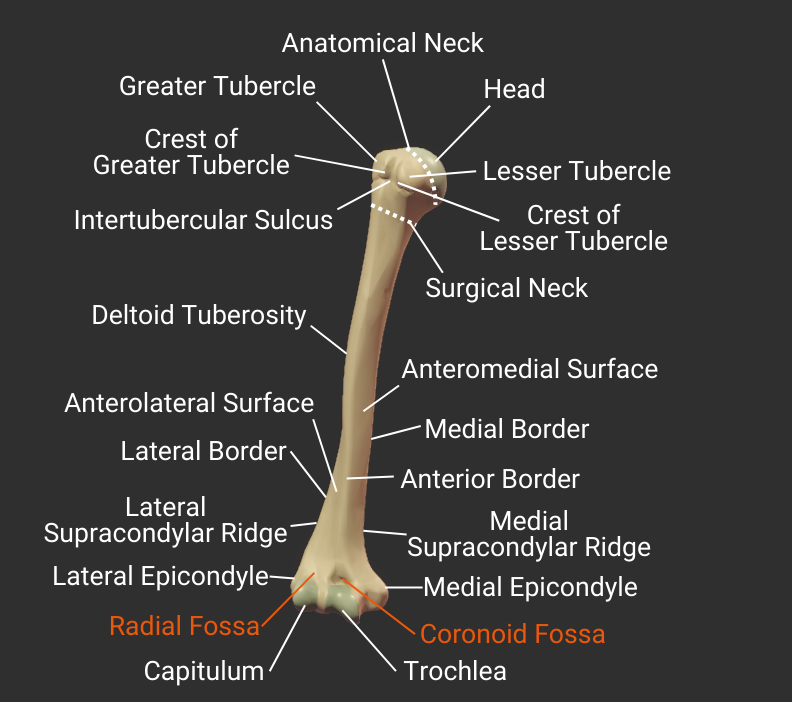
Fossas
Click the bulleted names for more information.
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
Radial Fossa
- Small anterior depression superior to the capitulum and lateral to the coronoid fossa
- Accommodates the radial head during elbow flexion
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
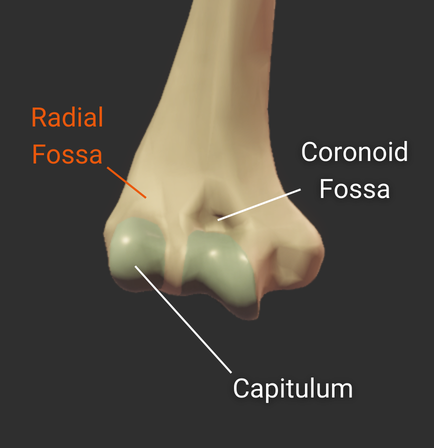
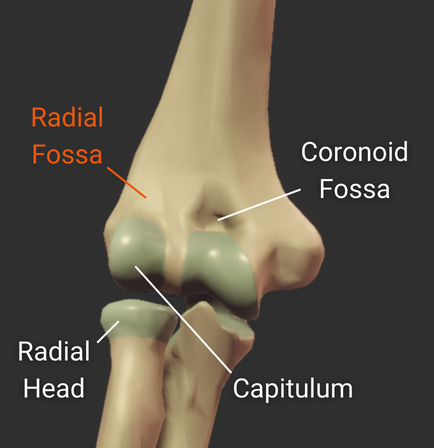
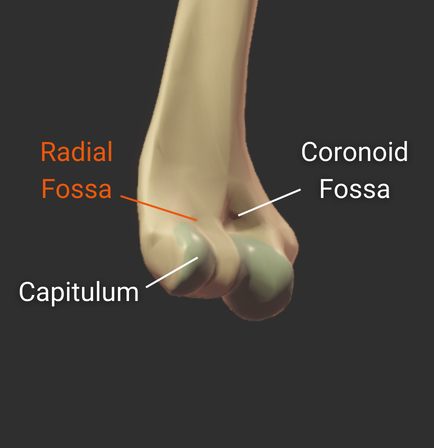
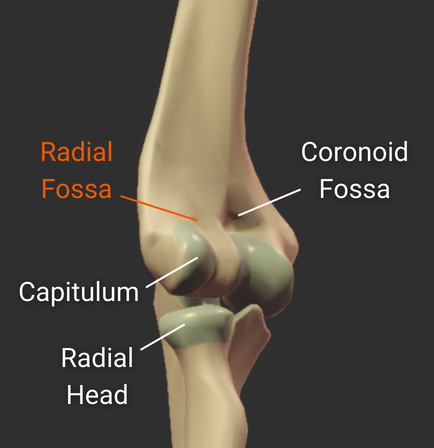
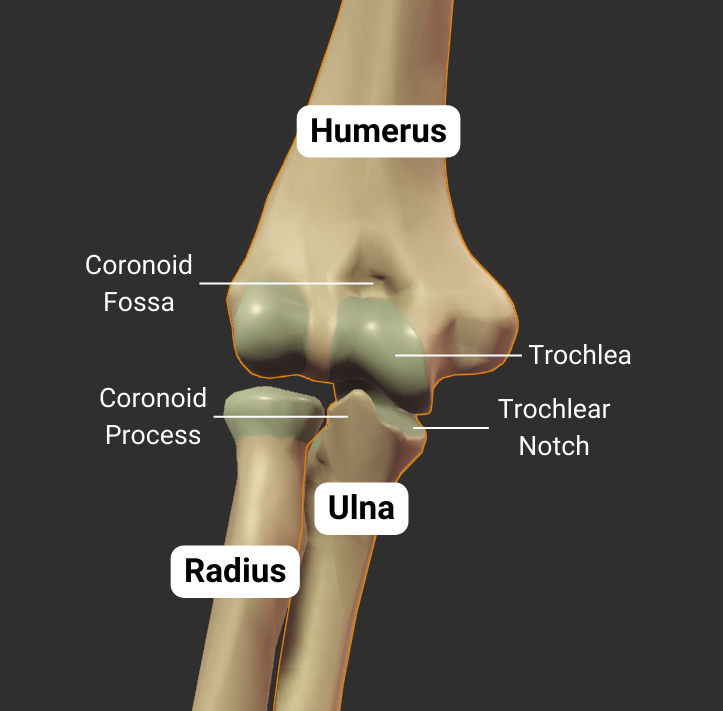
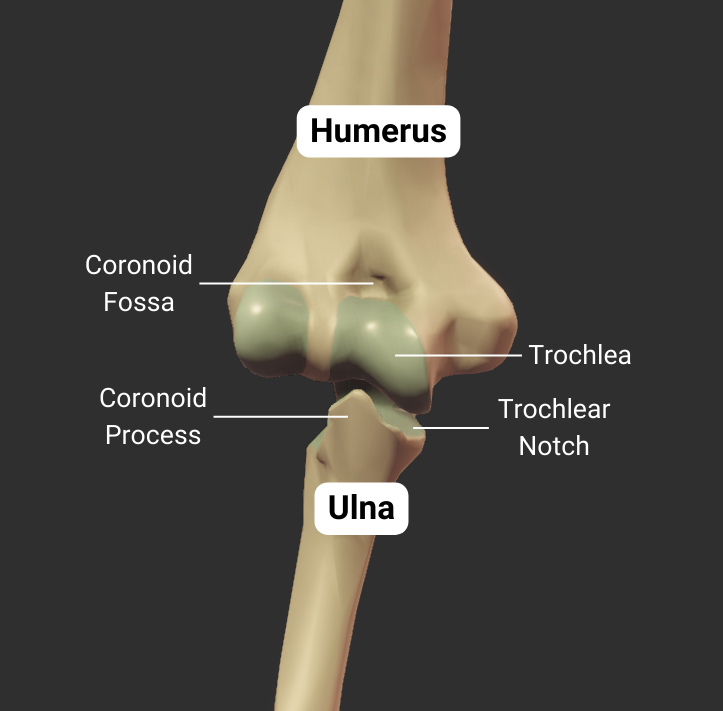
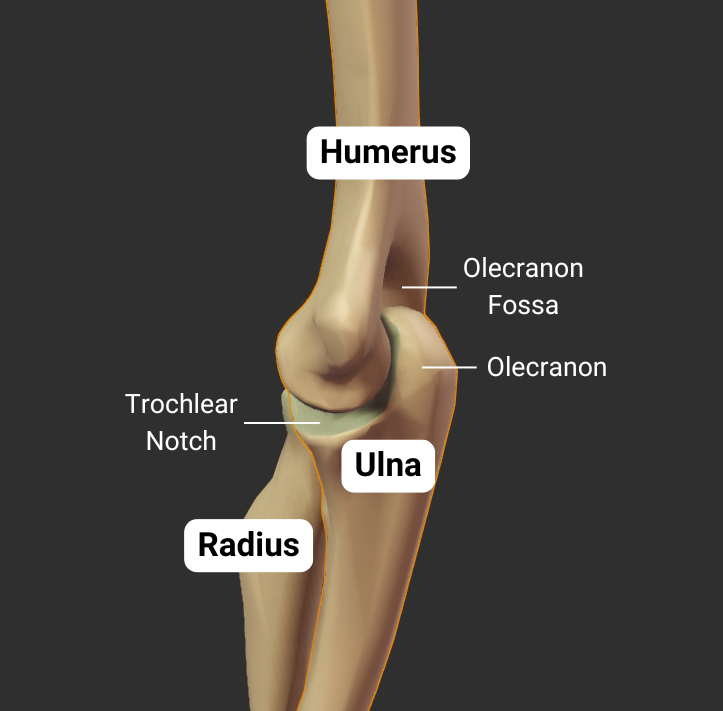
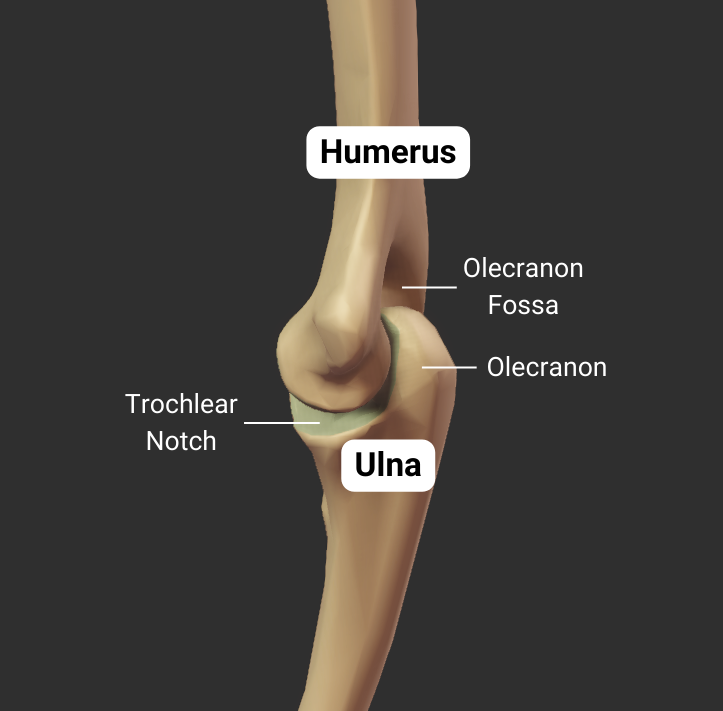
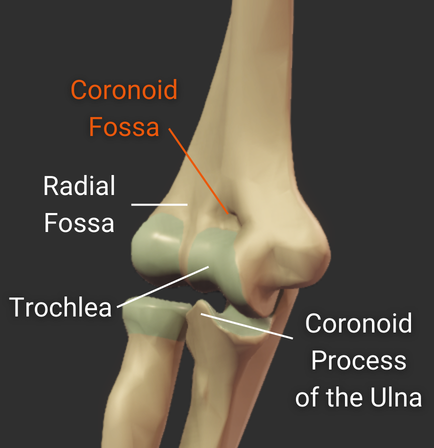
Coronoid Fossa
- Anterior depression superior to the trochlea
- Accommodates the ulna's coronoid process during deep elbow flexion
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
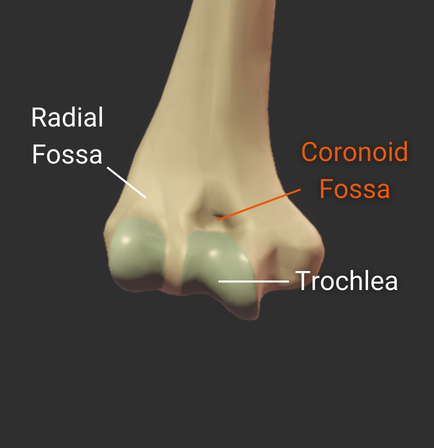
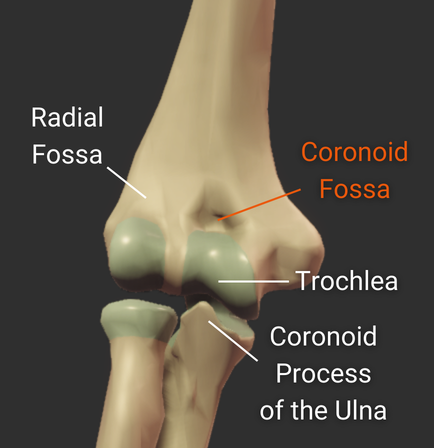
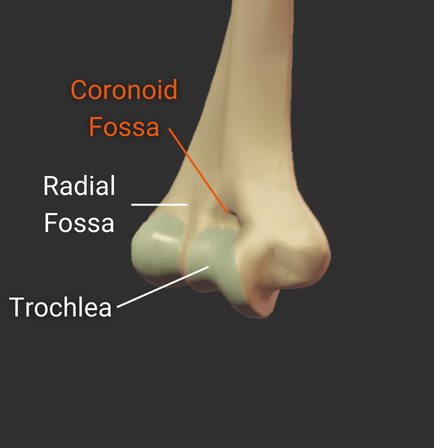
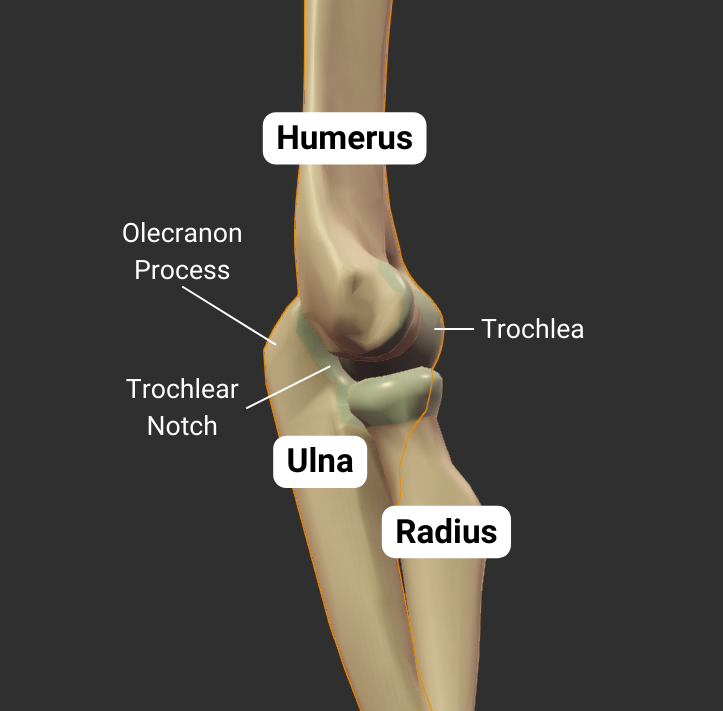
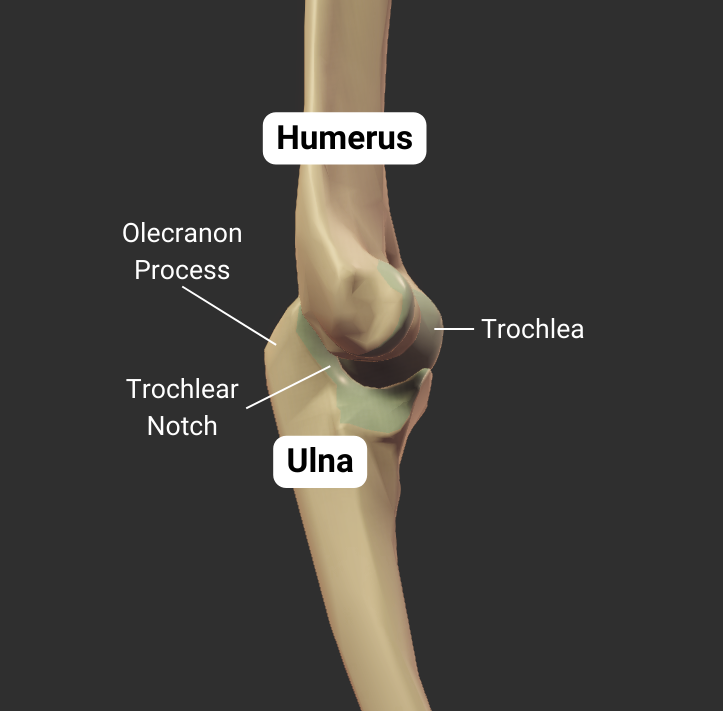
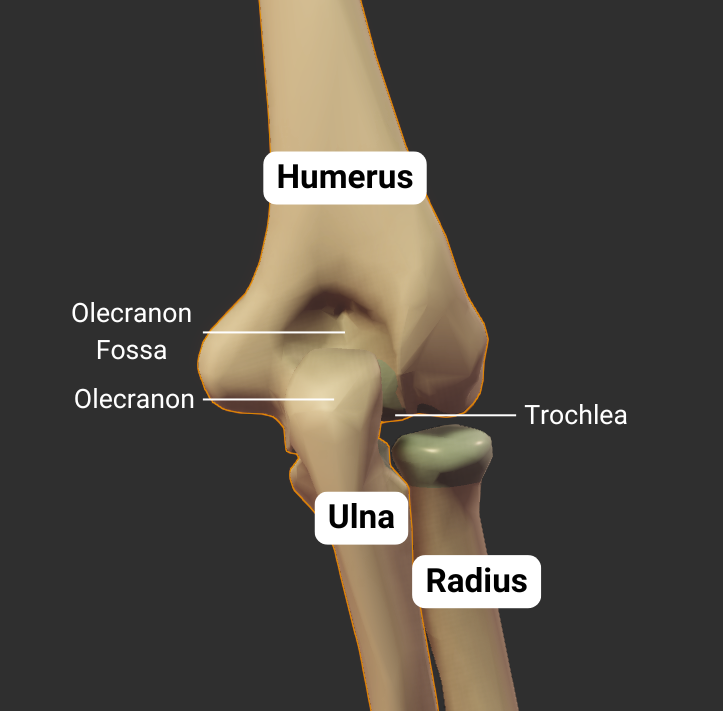
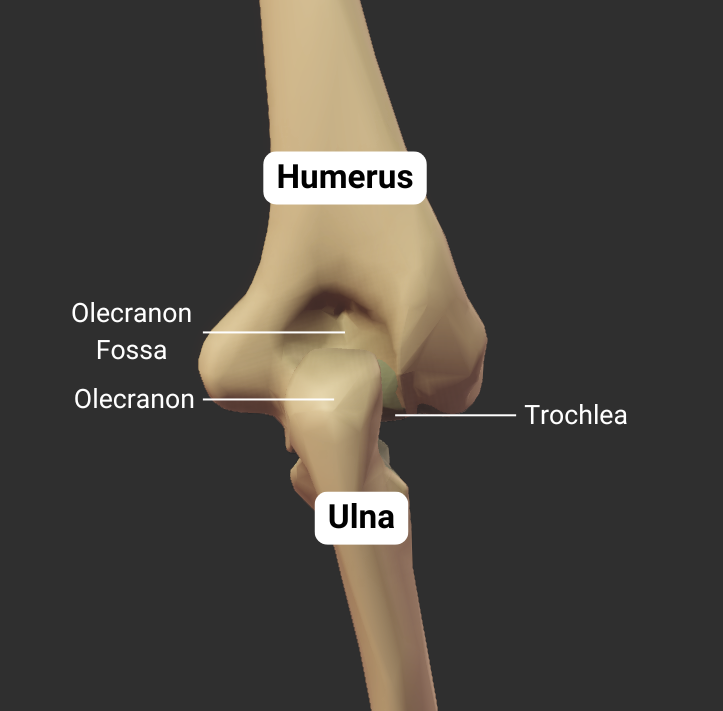
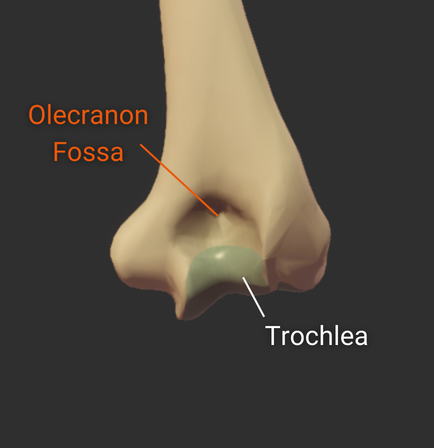
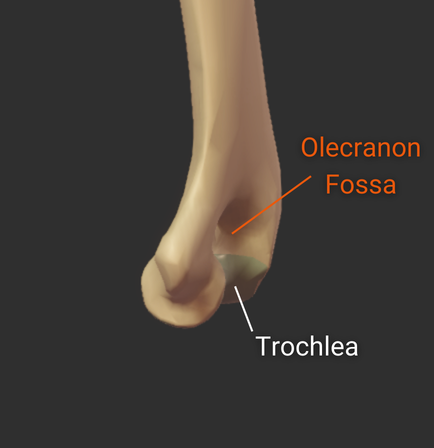
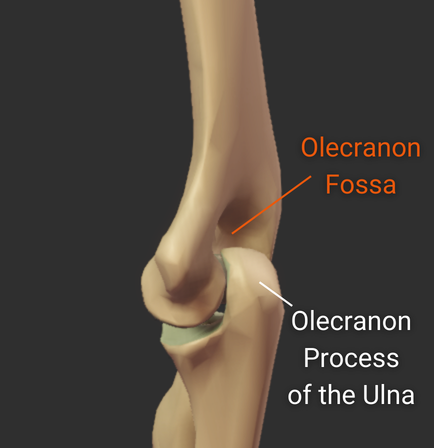
Olecranon Fossa
- Large posterior depression superior to the trochlea
- Accommodates the ulna's olecranon process during elbow extension
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
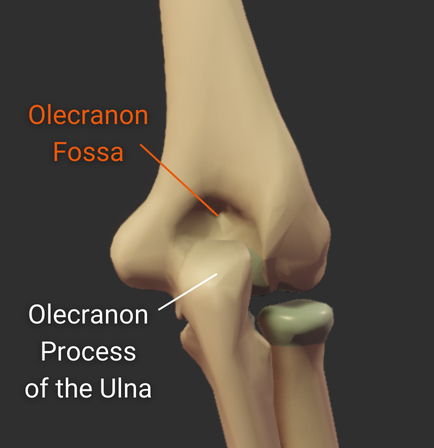
Distal Structures
Click the bulleted names for more information.
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
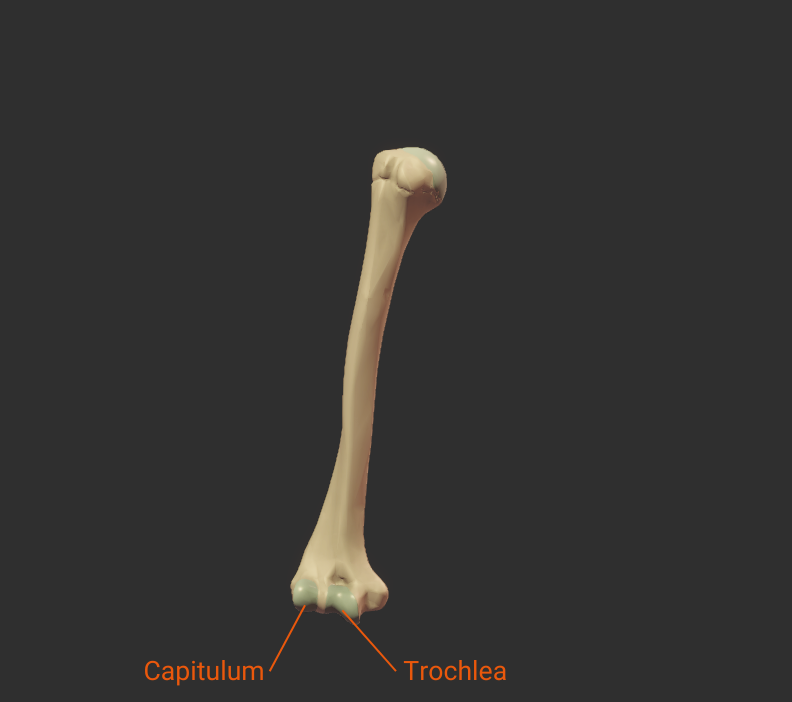
Trochlea
- Pulley-shaped structure on the humerus's distal end
- Articulates with the trochlear notch of the ulna
- Allows for hinge movement
- Medial to the humerus's capitulum
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.




Capitulum
- Rounded structure on the humerus's distal end
- Articulates with the head of the radius
- Allows for forearm rotation and flexion
- Lateral to the humerus's trochlea
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.




Condyle
- Name for the humerus's trochlea and capitulum when looked at together
- Forms the humerus's elbow joint surface
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.




Groove for the Ulnar Nerve
- Groove on the posterior surface of the medial epicondyle that the ulnar nerve runs through
- “Funny bone” area because striking this area compresses the ulnar nerve and leads to the "funny bone" sensation
- Also called the Cubital Groove
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.




Step 5 – Blood Supply
UNFINISHED
Plan: Write a description that gives an overview of the entire structure of blood vessels in the humerus. Then lead into breaking them up into proximal, shaft, and distal
NOTE: I have not yet verified that the arteries I have listed for the proximal region, shaft, and distal regions are correct
Proximal Region


Click the bulleted names for more information.
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
Anterior Circumflex Humeral Artery
- Do more research
- Supplies deltoid, teres minor, teres major, coracobrachialis, shoulder joint, head of humerus
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.


Posterior Circumflex Humeral Artery
- Do more research
- Supplies deltoid, teres minor, teres major, long/lateral heads of triceps brachii, shoulder joint, surrounding tissues
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.


Shaft


Click the bulleted names for more information.
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
Nutrient Artery of the Humerus
- Do more research
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.


Brachial Artery Branches
- Do more research
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.


Profunda Brachii Branches
- Do more research
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.


Distal Region


Click the bulleted names for more information.
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.
Radial Collateral Artery
- Do more research
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.


Middle Collateral Artery
- Do more research
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.


Superior Ulnar Collateral Artery
- Do more research
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.


Inferior Ulnar Collateral Artery
- Do more research
Click image to show/hide labels. Right click to enlarge.


References
Landmarks and General Anatomy
Muscles
- Kenhub – Supraspinatus Muscle
- Kenhub – Brachialis Muscle
- Kenhub – Upper Limb Muscles and Movements
- Kenhub – Arm Muscles
- Kenhub – Latissimus Dorsi Muscle
- Kenhub – Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
- Kenhub – Pronator Teres Muscle
Joints and Ligaments
- Kenhub – Elbow Joint
- Kenhub – Ligaments of the Upper Limb
- Kenhub – Head of Radius
- Kenhub – Proximal Radioulnar Joint
- Anatomy.co.uk – Humeroulnar Joint
- Anatomy.co.uk – Humeroradial Joint
Nerves
Arteries
Images
All images taken from Z-Anatomy. As of the date this was written (February 2, 2026), Z-Anatomy has a CC-BY-SA 4.0 License.
Feedback
We’d love to hear from you! You can: